Kubernetes Dashboard is a web-based user interface that allows users to manage and monitor Kubernetes clusters. It provides a graphical interface for performing common Kubernetes tasks, such as deploying applications, inspecting resources, and troubleshooting issues. Kubernetes Dashboard makes it easier for users to interact with and control their containerized applications and infrastructure. It is especially useful for users who prefer a graphical interface over command-line tools or who are new to Kubernetes and want an intuitive way to get started.
In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Kubernetes Dashboard using Helm on Ubuntu 22.04.
Prerequisites
- A server running Ubuntu 22.04 with Kubernetes installed
Step 1 – Add Kubernetes Dashboard Repo
Helm is not included by default in the Ubuntu default repo, so you will need to install it using a script.
First, download the Helm installation script.
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
Next, make the downloaded script executable.
chmod 700 get_helm.sh
Next, run the script to install Helm.
./get_helm.sh
Next, add the Kubernetes Dashboard repo using Helm.
helm repo add kubernetes-dashboard https://kubernetes.github.io/dashboard/
You can verify the added repo using the following command:
helm repo list
Output:
NAME URL kubernetes-dashboard https://kubernetes.github.io/dashboard/
Step 2 – Install Kubernetes Dashboard Using Helm
Now you can install Kubernetes Dashboard chart using Helm. You may want to specify a release name and namespace during installation.
helm upgrade --install kubernetes-dashboard kubernetes-dashboard/kubernetes-dashboard --create-namespace --namespace kubernetes-dashboard
Output:
*************************************************************************************************
*** PLEASE BE PATIENT: Kubernetes Dashboard may need a few minutes to get up and become ready ***
*************************************************************************************************
Congratulations! You have just installed Kubernetes Dashboard in your cluster.
To access Dashboard run:
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard port-forward svc/kubernetes-dashboard-kong-proxy 8443:443
NOTE: In case port-forward command does not work, make sure that kong service name is correct.
Check the services in Kubernetes Dashboard namespace using:
kubectl -n kubernetes-dashboard get svc
Dashboard will be available at:
https://localhost:8443
Once Kubernetes Dashboard is installed, you can verify it using the following command:
kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboard
Output:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE kubernetes-dashboard-web ClusterIP 10.43.128.204 8000/TCP 12m kubernetes-dashboard-kong-manager NodePort 10.43.163.11 8002:32281/TCP,8445:31992/TCP 12m kubernetes-dashboard-auth ClusterIP 10.43.141.160 8000/TCP 12m kubernetes-dashboard-metrics-scraper ClusterIP 10.43.159.40 8000/TCP 12m kubernetes-dashboard-api ClusterIP 10.43.8.225 8000/TCP 12m kubernetes-dashboard-kong-proxy ClusterIP 10.43.208.190 443/TCP 12m
Step 3 – Generate Token for Kubernetes Dashboard
Now, you will need to generate a token to access Kubernetes Dashboard.
First, create a Kubernetes manifest file to create a service account.
nano k8s-dashboard-account.yaml
Add the following content:
apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: admin-user namespace: kube-system --- apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRoleBinding metadata: name: admin-user roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: ClusterRole name: cluster-admin subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: admin-user namespace: kube-system
Next, apply the above configuration to the Kubernetes cluster.
kubectl create -f k8s-dashboard-account.yaml
Next, generate a token using the following command:
kubectl -n kube-system create token admin-user
Output:
eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsImtpZCI6IkIwbk5FWE0zVXppQV9aVWEyMndzRlNnMllIREpldUdVckVZdzFqUzcwalEifQ.eyJhdWQiOlsiaHR0cHM6Ly9rdWJlcm5ldGVzLmRlZmF1bHQuc3ZjLmNsdXN0ZXIubG9jYWwiLCJrM3MiXSwiZXhwIjoxNzExMTcwMjQwLCJpYXQiOjE3MTExNjY2NDAsImlzcyI6Imh0dHBzOi8va3ViZXJuZXRlcy5kZWZhdWx0LnN2Yy5jbHVzdGVyLmxvY2FsIiwia3ViZXJuZXRlcy5pbyI6eyJuYW1lc3BhY2UiOiJrdWJlLXN5c3RlbSIsInNlcnZpY2VhY2NvdW50Ijp7Im5hbWUiOiJhZG1pbi11c2VyIiwidWlkIjoiNTNhNjdhNjYtNDAyOC00MTFlLWI5YTctMzViZDJkYzUwOTc2In19LCJuYmYiOjE3MTExNjY2NDAsInN1YiI6InN5c3RlbTpzZXJ2aWNlYWNjb3VudDprdWJlLXN5c3RlbTphZG1pbi11c2VyIn0.XrTJC9WhaZrhRuo2buBXy48AnaGxsjHcLNCZpjpcXF5UQagR3GQgCpyArWWuGaw8Wu_-bCzHknsZ1oQ4kDLnwCrtgnG3bg18axuodvydMivw2iETtEZNTRJF989amM8fdO3xSQgNh9O59UjiebUtNNQ45d2Rmzxq1VoVpsL0hx9D0WIg-7iUZ305OKjufIBWx0nW_VBRaBE4kLWj3t7ykJdIE9qE0s12s7XjUnLvA1DWFWC_SoG08q8q4Y0LdThKz8wzVI87DR4KTlTTuSPJEZkI5hcZu02SkKaleNBYnFlabBD1IWXK18uY_5LAIFrjDgkCPUysCbAA_7F87dZ4sg
Step 4 – Access Kubernetes Dashboard
To access Kubernetes Dashboard from the outside network, you will need to expose it using the port forward method. Run the following command to expose Kubernetes Dashboard.
kubectl port-forward -n kubernetes-dashboard service/kubernetes-dashboard-kong-proxy 10443:443 --address 0.0.0.0 &
You will see the following output:
Forwarding from 0.0.0.0:10443 -> 8443
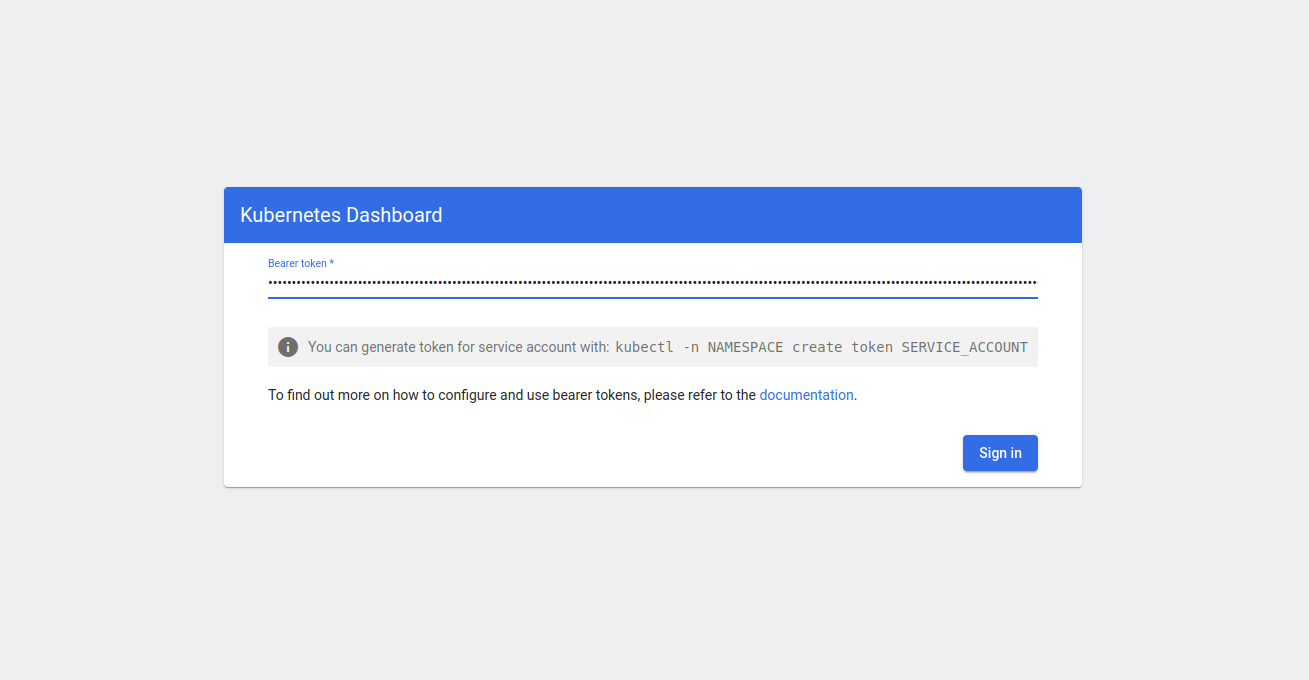
Now, open your web browser and access Kubernetes Dashboard using the URL https://server-ip:10443. You will be asked to enter a token to log in.
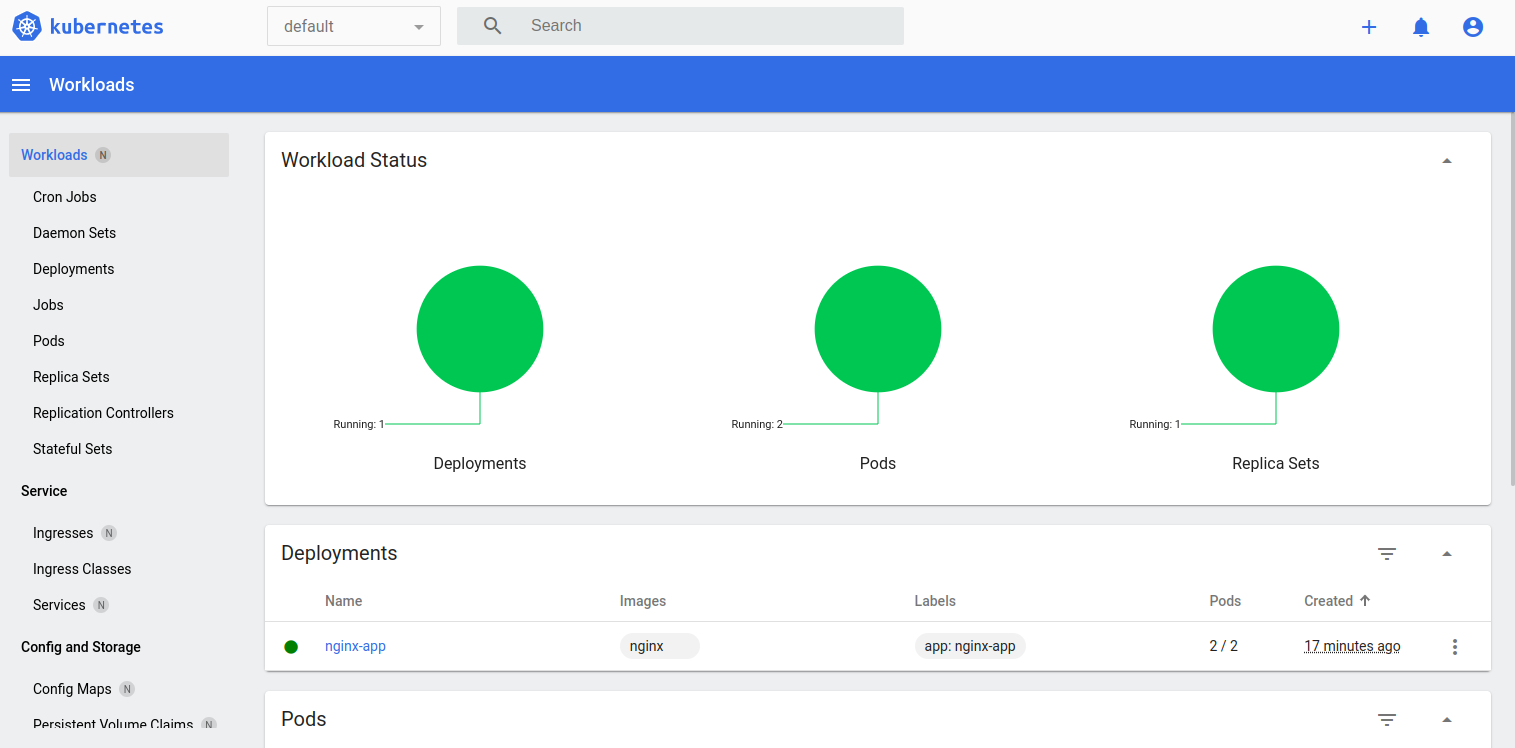
Provide your generated token and click on Sign in. You will see Kubernetes Dashboard on the following screen.
Conclusion
In this guide, you learned how to install Kubernetes Dashboard using Helm on Ubuntu 22.04. You can now manage and monitor Kubernetes pods, services, and logs via Kubernetes Dashboard. You can now start managing your Kubernetes cluster using Kubernetes Dashboard on dedicated server hosting from Atlantic.Net!