Monit is a free, open-source, lightweight monitoring tool used to manage and monitor services on Linux operating systems. Monit allows you to check the status of processes, files, directories, checksums, permissions, and filesystems via the command line interface. If something is wrong, Monit can notify you instantly via email. It has the ability to automatically start a process if it’s not running, restart one if it’s not responding, and stop a process if it’s consuming too many resources.
In this post, we will show you how to install and use the Monit monitoring tool on Arch Linux.
Step 1 – Configure Repository
By default, the default repository is outdated in Arch Linux, so you will need to modify the default mirror list. You can do it by editing the mirrorlist configuration file:
nano /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist
Remove all lines and add the following lines:
## Score: 0.7, United States Server = http://mirror.us.leaseweb.net/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 0.8, United States Server = http://lug.mtu.edu/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch Server = http://mirror.nl.leaseweb.net/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 0.9, United Kingdom Server = http://mirror.bytemark.co.uk/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 1.5, United Kingdom Server = http://mirrors.manchester.m247.com/arch-linux/$repo/os/$arch Server = http://archlinux.dcc.fc.up.pt/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 6.6, United States Server = http://mirror.cs.pitt.edu/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 6.7, United States Server = http://mirrors.acm.wpi.edu/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 6.8, United States Server = http://ftp.osuosl.org/pub/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 7.1, India Server = http://mirror.cse.iitk.ac.in/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 10.1, United States Server = http://mirrors.xmission.com/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch
Save and close the file, then update all the package indexes with the following command:
pacman -Syu
Step 2 – Install Monit Monitoring Tool
By default, the Monit package is included in the Arch Linux default repository. You can install it easily using the following command.
pacman -S monit
Once Monit is installed, start the Monit service and enable it to start at system reboot.
systemctl start monit systemctl enable monit
To check the status of Monit, run the following command.
systemctl status monit
You should see the following output.
● monit.service - Pro-active monitoring utility for unix systems
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/monit.service; disabled; preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2023-01-04 22:14:35 EST; 4s ago
Docs: man:monit(1)
https://mmonit.com/wiki/Monit/HowTo
Main PID: 72648 (monit)
Tasks: 2 (limit: 2362)
Memory: 2.2M
CGroup: /system.slice/monit.service
└─72648 /usr/bin/monit -I
Jan 04 22:14:35 archlinux systemd[1]: Started Pro-active monitoring utility for unix systems.
Jan 04 22:14:35 archlinux monit[72648]: New Monit id: c0a3ed9c326d12711c321547eeb05f41
Stored in '/root/.monit.id'
Jan 04 22:14:35 archlinux monit[72648]: Starting Monit 5.32.0 daemon with http interface at [localhost]:2812
Jan 04 22:14:35 archlinux monit[72648]: 'archlinux' Monit 5.32.0 started
Step 3 – Configure Monit
Monit also provides a web interface to monitor your system and services. However, it is disabled by default. You can enable it by editing the Monit default configuration file.
nano /etc/monitrc
Change the following lines to enable the web interface and define the Monit admin username and password.
set httpd port 2812 and
use address your-server-ip
# allow localhost
allow admin:monit
Save and close the file, then verify the Monit configuration file with the following command.
monit -t
You will get the following output.
Control file syntax OK
Next, restart the Monit service to apply the changes.
systemctl restart monit
At this point, the Monit web interface is enabled and listens on port 2812. You can check it with the following command.
ss -plunt | grep 2812
You should see the following output.
tcp LISTEN 0 0 127.0.0.1:2812 0.0.0.0:* users:(("monit",pid=72668,fd=5))
tcp LISTEN 0 0 [::1]:2812 *:* users:(("monit",pid=72668,fd=6))
Step 4 – Monitor Linux System Via Command Line
Monit provides a command line tool to monitor your Linux system via cli.
To check your system information, run the following command.
monit status
You should get the following information.
Monit 5.32.0 uptime: 0m System 'archlinux' status OK monitoring status Monitored monitoring mode active on reboot start load average [0.01] [0.01] [0.00] cpu 0.0%usr 0.0%sys 0.0%nice 0.0%iowait 0.0%hardirq 0.0%softirq 0.0%steal 0.0%guest 0.0%guestnice memory usage 270.5 MB [13.6%] swap usage 0 B [0.0%] uptime 18h 38m boot time Wed, 04 Jan 2023 03:38:23 filedescriptors 1024 [0.0% of 9223372036854775807 limit] data collected Wed, 04 Jan 2023 22:16:42
Step 5 – Monitor Apache Service with Monit
First, the Apache package must be installed on your server. If not installed, you can install it with the following command.
pacman -S apache
Once the Apache package is installed, start and enable the Apache service with the following command:
systemctl start httpd systemctl enable httpd
Next, edit the Monit configuration file.
nano /etc/monitrc
Add/modify the following lines to define your Apache server.
#set log syslog
set log /var/log/monit.log
check process apache with pidfile /var/run/httpd/httpd.pid
start program = "/usr/bin/systemctl start httpd" with timeout 60 seconds
stop program = "/usr/bin/systemctl stop httpd"
if cpu > 60% for 2 cycles then alert
if cpu > 80% for 5 cycles then restart
if totalmem > 200.0 MB for 5 cycles then restart
if children > 250 then restart
if disk read > 500 kb/s for 10 cycles then alert
if disk write > 500 kb/s for 10 cycles then alert
Save and close the file, then restart the Monit service to apply the changes.
systemctl restart monit
You can now verify your Apache service status using the following command.
monit summary
You will get the following output.
Monit 5.32.0 uptime: 0m ┌─────────────────────────────────┬────────────────────────────┬───────────────┐ │ Service Name │ Status │ Type │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ archlinux │ OK │ System │ ├─────────────────────────────────┼────────────────────────────┼───────────────┤ │ apache │ OK │ Process │ └─────────────────────────────────┴────────────────────────────┴───────────────┘
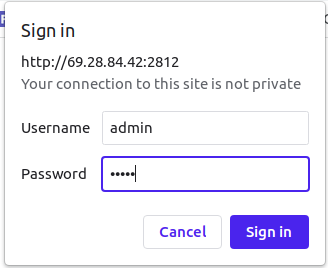
You can also monitor your Apache via web interface using the URL http://your-server-ip:2812. You should see the Monit login page.
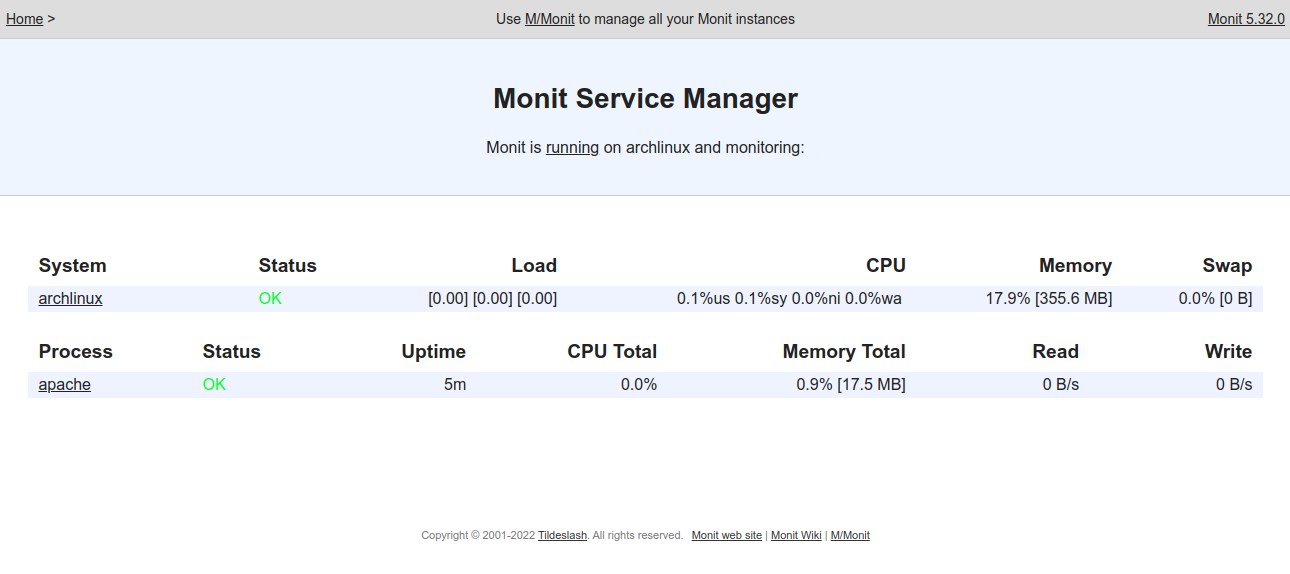
Provide your Monit admin username and password and click on the Sign In button. You should see the Monit dashboard on the following screen.
Now, stop the Apache service and check how Monit can start the Apache service automatically.
systemctl stop httpd
You can now check the Monit logs using the following command.
tail -f /var/log/monit.log
You should see that Monit starts the Apache service automatically.
[2023-01-04T22:46:15-0500] info : Starting Monit 5.32.0 daemon with http interface at [localhost]:2812 [2023-01-04T22:46:15-0500] info : 'archlinux' Monit 5.32.0 started [2023-01-04T22:46:45-0500] error : 'apache' process is not running [2023-01-04T22:46:45-0500] info : 'apache' trying to restart [2023-01-04T22:46:45-0500] info : 'apache' start: '/usr/bin/systemctl start httpd'
Conclusion
In this post, we showed you how to install Monit on Arch Linux. We also showed you how to monitor Apache service using Monit. You can now add more services to the Monit configuration and monitor them via the Monit dashboard. You can also deploy the Monit monitoring tool on dedicated server hosting from Atlantic.Net!