Sails.js is an open-source MVC back-end web framework built on top of JavaScript runtime. It allows developers to create custom, enterprise-grade Node.js apps quickly. It offers a modern approach to building web applications with real-time features, such as a live chat option for smooth customer experiences. It also allows you to share your code between the server and the client.
This post will show you how to install Sails.js with Nginx on Fedora Linux.
Step 1 – Install Nodejs
First, update the server and install the required dependencies using the following commands.
dnf update -y
dnf install curl gcc-c++ make -y
Next, add the Nodesource repository using the following command.
curl -sL https://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_18.x | bash -
Next, install the Node.js package with the following command.
dnf install nodejs -y
You can now verify the Node.js installation using the following command.
node --version
Output:
v18.19.0
Step 2 – Install Sailsjs Framework
You can use the NPM command line tool to install the Sails.js easily, as shown below.
npm -g install sails
Once Sails.js is installed, you can verify its version with the following command.
sails --version
Output.
1.5.8
Step 3 – Create an Application with Sailsjs
Sails.js provides an easier way to create an application via the command line terminal. Let’s make an application called sailsapp with the following command.
sails new sailsapp
You will be asked to choose a template for your application.
Choose a template for your new Sails app: 1. Web App · Extensible project with auth, login, & password recovery 2. Empty · An empty Sails app, yours to configure (type "?" for help, or <CTRL+C> to cancel) ? 2
Type 2 and press the Enter key to create an application.
info: Installing dependencies...
Press CTRL+C to cancel.
(to skip this step in the future, use --fast)
------------------------------------------------------------
Cancelled `npm install`.
New app was generated successfully, but some dependencies
in node_modules/ are probably still incomplete or missing.
Before you can lift this app, you'll need to cd in and run:
rm -rf node_modules && npm install
For more help, visit https://sailsjs.com/support.
Next, change the directory to your application directory and remove the node modules.
cd sailsapp rm -rf node_modules
Next, install all the required dependencies using the NPM command.
npm install
Finally, start your application with the following command.
sails lift
You will see the following output.
info: Starting app... info: info: .-..-. info: info: Sails <| .-..-. info: v1.5.8 |\ info: /|.\ info: / || \ info: ,' |' \ info: .-'.-==|/_--' info: `--'-------' info: __---___--___---___--___---___--___ info: ____---___--___---___--___---___--___-__ info: info: Server lifted in `/root/sailsapp` info: To shut down Sails, press + C at any time. info: Read more at https://sailsjs.com/support. debug: ------------------------------------------------------- debug: :: Wed Sep 13 2023 11:25:30 GMT-0400 (Eastern Daylight Time) debug: Environment : development debug: Port : 1337 debug: Local : http://localhost:1337 debug: -------------------------------------------------------
Press the CTRL+C to stop the application.
Step 4 – Create a Systemd Service File for Sailsjs
Next, create a systemd service file to manage your application.
nano /lib/systemd/system/sails.service
Add the following configurations.
[Unit] After=network.target [Service] Type=simple User=root WorkingDirectory=/root/sailsapp ExecStart=/usr/bin/sails lift Restart=on-failure [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file, then reload the systemd daemon.
systemctl daemon-reload
Next, start and enable the Sails.js service.
systemctl start sails systemctl enable sails
You can also verify the status of your Sails.js service using the following command.
systemctl status sails
Output:
● sails.service
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/sails.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2023-09-13 11:26:03 EDT; 5s ago
Main PID: 2499 (node)
Tasks: 22 (limit: 4666)
Memory: 162.4M
CPU: 4.090s
CGroup: /system.slice/sails.service
├─2499 node /usr/bin/sails lift
└─2507 grunt
Sep 13 11:26:05 fedora sails[2499]: info:
Sep 13 11:26:05 fedora sails[2499]: info: Server lifted in `/root/sailsapp`
Sep 13 11:26:05 fedora sails[2499]: info: To shut down Sails, press + C at any time.
Sep 13 11:26:05 fedora sails[2499]: info: Read more at https://sailsjs.com/support.
Sep 13 11:26:05 fedora sails[2499]: debug: -------------------------------------------------------
Sep 13 11:26:05 fedora sails[2499]: debug: :: Wed Sep 13 2023 11:26:05 GMT-0400 (Eastern Daylight Time)
Sep 13 11:26:05 fedora sails[2499]: debug: Environment : development
Sep 13 11:26:05 fedora sails[2499]: debug: Port : 1337
Sep 13 11:26:05 fedora sails[2499]: debug: Local : http://localhost:1337
Sep 13 11:26:05 fedora sails[2499]: debug: -------------------------------------------------------
Step 5 – Configure Nginx as a Reverse Proxy for Sailsjs
You must configure the Nginx as a reverse proxy to access your application from the remote machine.
First, install the Nginx server.
dnf install nginx -y
Next, create an Nginx configuration file.
nano /etc/nginx/conf.d/sails.conf
Add the following configurations.
server {
listen 80;
server_name sails.example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:1337/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_buffering off;
}
}
Save and close the file, then edit the Nginx main configuration file.
nano /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
Add the following line after the line http{:
server_names_hash_bucket_size 64;
Save and close the file, then verify the Nginx configuration.
nginx -t
You should get the following output:
nginx: the configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf syntax is ok nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test is successful
Finally, start and enable the Nginx service with the following command.
systemctl start nginx systemctl enable nginx
Step 6 – Access Sailsjs Application
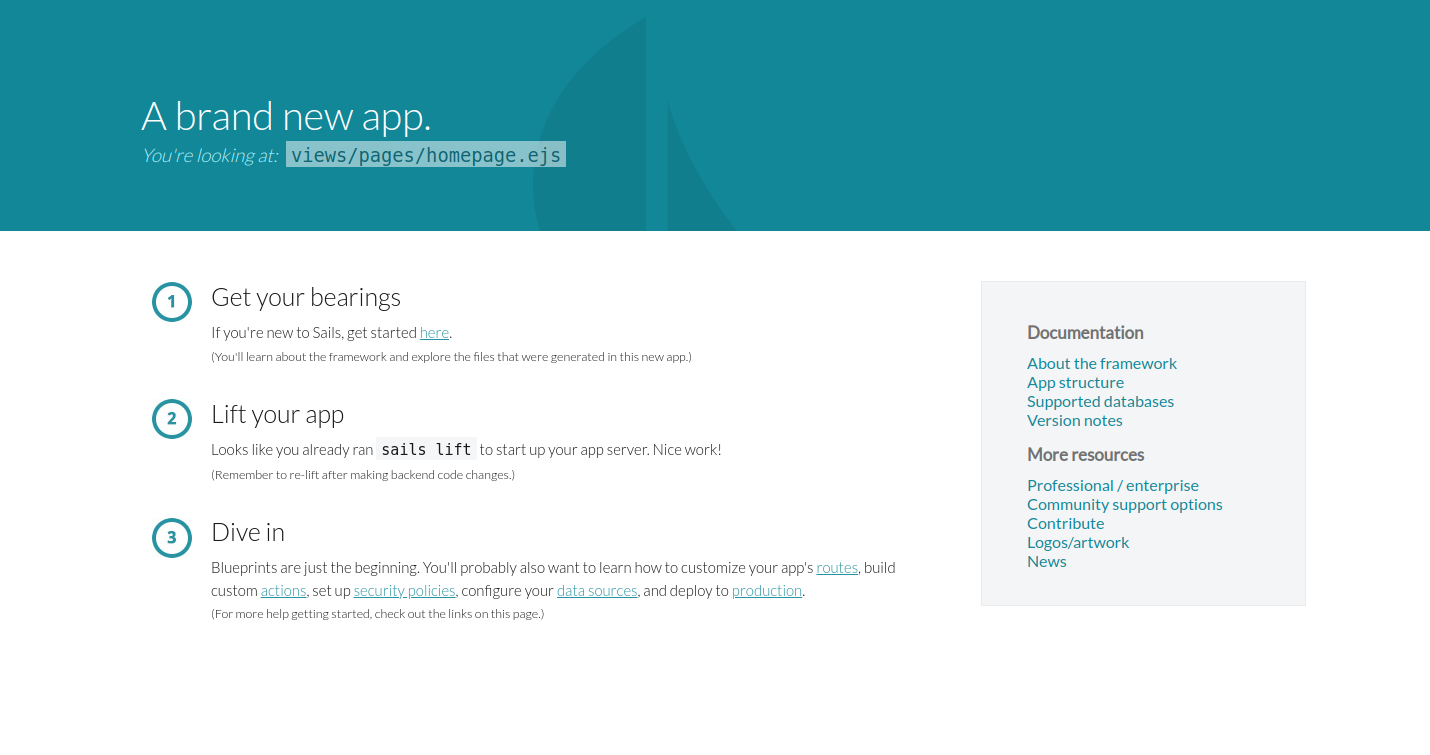
At this point, the Sails.js application is installed on your server. You can now access it using the URL http://sails.example.com. You will see the Sails.js default dashboard on the following screen.
Conclusion
This tutorial explained installing and creating a Sails.js application on Fedora Linux. We also showed you how to configure the Nginx as a reverse proxy to access the application from the outside world. You can now try to deploy the Sails.js application on dedicated server hosting from Atlantic.Net!