Apache Tomcat is an open-source Java servlet container used to host Java-based web applications. It is a popular choice for web developers to build and maintain dynamic websites and applications based on the Java software platform. Apache Tomcat is fast and lightweight, and it is much better than the alternative options.
In this post, we will explain how to install Apache Tomcat 10 on Arch Linux.
Step 1 – Configure Repository
By default, the default repository is outdated in Arch Linux, so you will need to modify the default mirror list. You can do it by editing the mirrorlist configuration file:
nano /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist
Remove all lines and add the following lines:
## Score: 0.7, United States Server = http://mirror.us.leaseweb.net/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 0.8, United States Server = http://lug.mtu.edu/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch Server = http://mirror.nl.leaseweb.net/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 0.9, United Kingdom Server = http://mirror.bytemark.co.uk/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 1.5, United Kingdom Server = http://mirrors.manchester.m247.com/arch-linux/$repo/os/$arch Server = http://archlinux.dcc.fc.up.pt/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 6.6, United States Server = http://mirror.cs.pitt.edu/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 6.7, United States Server = http://mirrors.acm.wpi.edu/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 6.8, United States Server = http://ftp.osuosl.org/pub/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 7.1, India Server = http://mirror.cse.iitk.ac.in/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch ## Score: 10.1, United States Server = http://mirrors.xmission.com/archlinux/$repo/os/$arch
Save and close the file then update all the package indexes with the following command:
pacman -Syu
Step 2 – Install Java JDK
Apache Tomcat is a Java-based application, so Java must be installed on your server. If not installed, you can install it using the following command:
pacman -S jre-openjdk-headless jre-openjdk jdk-openjdk openjdk-doc openjdk-src
After installing Java, verify the Java version with the following command:
java -version
Sample output:
openjdk version "18.0.2" 2022-07-19 OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 18.0.2+0) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 18.0.2+0, mixed mode)
Step 3 – Download Apache Tomcat 10
Before downloading Apache Tomcat, you will need to add a dedicated user for Tomcat. You can add it using the following command:
useradd -r -d /opt/tomcat/ -s /bin/false -c "Tomcat User" tomcat
Next, download the latest version of Apache Tomcat 10 using the following command:
wget https://dlcdn.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-10/v10.0.27/bin/apache-tomcat-10.0.27.tar.gz After downloading Apache Tomcat, create a directory for Tomcat and extract the downloaded file inside the /opt/tomcat directory:
mkdir /opt/tomcat tar xzf apache-tomcat-10.0.27.tar.gz -C /opt/tomcat --strip-components=1
Next, change the ownership of /opt/tomcat directory to tomcat:
chown -R tomcat: /opt/tomcat/
Step 4 – Configure Tomcat Admin User
Next, you will need to create an admin user for managing Tomcat Manager and the Host Manager app. You can do it by editing the /opt/tomcat/conf/tomcat-users.xml file:
nano /opt/tomcat/conf/tomcat-users.xml
Add the following lines just above the last line:
<role rolename="manager-gui"/> <user username="admin" password="password" roles="manager-gui,admin-gui"/>
Save and close the file when you are finished.
Step 5 – Configure Tomcat for Remote Host
By default, Tomcat can be accessed only from the localhost, so you will need to configure Tomcat to access it from the remote host.
To access the Manager from the remote host, edit the context.xml file:
nano /opt/tomcat/webapps/manager/META-INF/context.xml
Remove the following lines:
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteAddrValve"
allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::1|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1" />
Save and close the file when you are finished.
To access the Host Manager from the remote host, edit the context.xml file:
nano /opt/tomcat/webapps/host-manager/META-INF/context.xml
Remove the following lines:
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.RemoteAddrValve"
allow="127\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+|::1|0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1" />
Save and close the file when you are finished.
Step 6 – Create a Systemd Unit File for Apache Tomcat
Next, it is recommended to create a systemd unit file to manage the Tomcat service. You can create it with the following command:
nano /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service
Add the following lines:
[Unit] Description=Apache Tomcat Server After=syslog.target network.target [Service] Type=forking User=tomcat Group=tomcat Environment=CATALINA_PID=/opt/tomcat/temp/tomcat.pid Environment=CATALINA_HOME=/opt/tomcat Environment=CATALINA_BASE=/opt/tomcat ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/bin/catalina.sh start ExecStop=/opt/tomcat/bin/catalina.sh stop RestartSec=10 Restart=always [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file, then reload the systemd daemon with the following command:
systemctl daemon-reload
Next, start the Tomcat service and enable it to start at system reboot:
systemctl start tomcat systemctl enable tomcat
You can verify the status of the Tomcat service with the following command:
systemctl status tomcat
Sample output:
● tomcat.service - Apache Tomcat Server
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service; disabled; preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2022-10-08 03:13:21 UTC; 6s ago
Process: 50206 ExecStart=/opt/tomcat/bin/catalina.sh start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 50218 (java)
Tasks: 30 (limit: 2362)
Memory: 77.6M
CGroup: /system.slice/tomcat.service
└─50218 /usr/bin/java -Djava.util.logging.config.file=/opt/tomcat/conf/logging.properties -Djava.util.logging.manager=org.apache>
Oct 08 03:13:21 archlinux systemd[1]: Starting Apache Tomcat Server...
Oct 08 03:13:21 archlinux catalina.sh[50206]: Tomcat started.
Oct 08 03:13:21 archlinux systemd[1]: Started Apache Tomcat Server.
Step 7 – Access Apache Tomcat Web UI
At this point, Apache Tomcat is started and listening on port 8080. You can check it with the following command:
ss -antpl | grep 8080
Sample output:
LISTEN 0 0 *:8080 *:* users:(("java",pid=50218,fd=41))
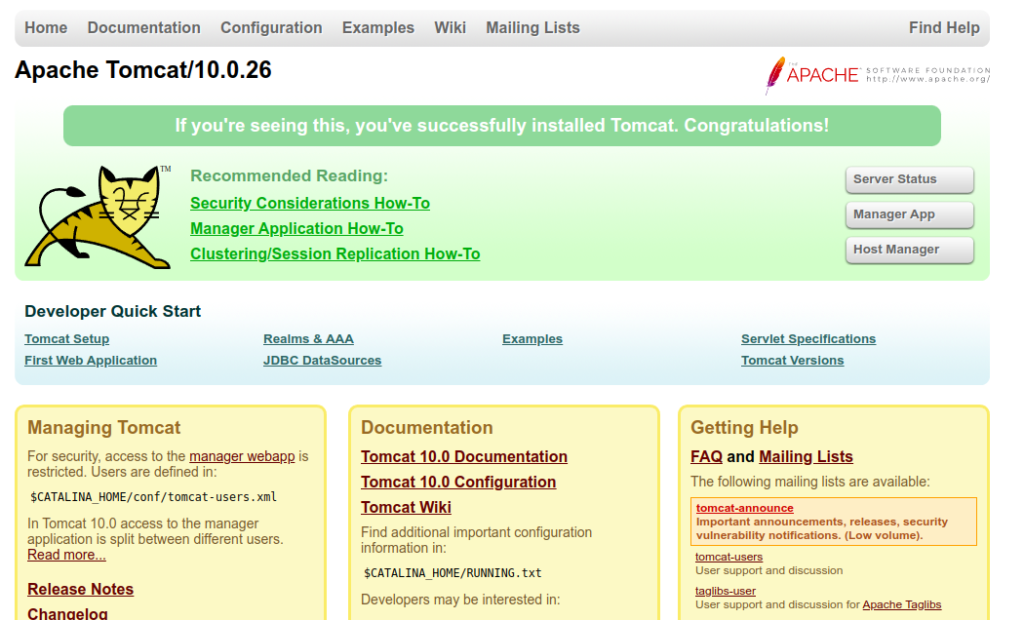
You can now access the Tomcat using the URL http://your-server-ip:8080. You should see the following screen:
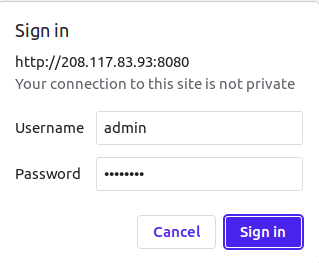
To access the Manager App, click on the Manager. You will be asked to provide an admin user and password as shown below:
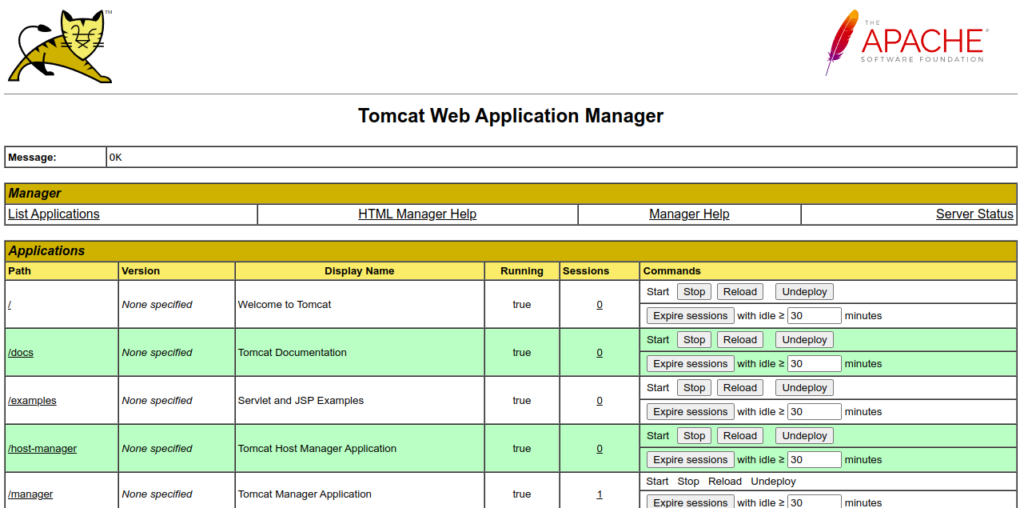
Provide your admin username and password and click on the Sign in button. You should see the following screen:
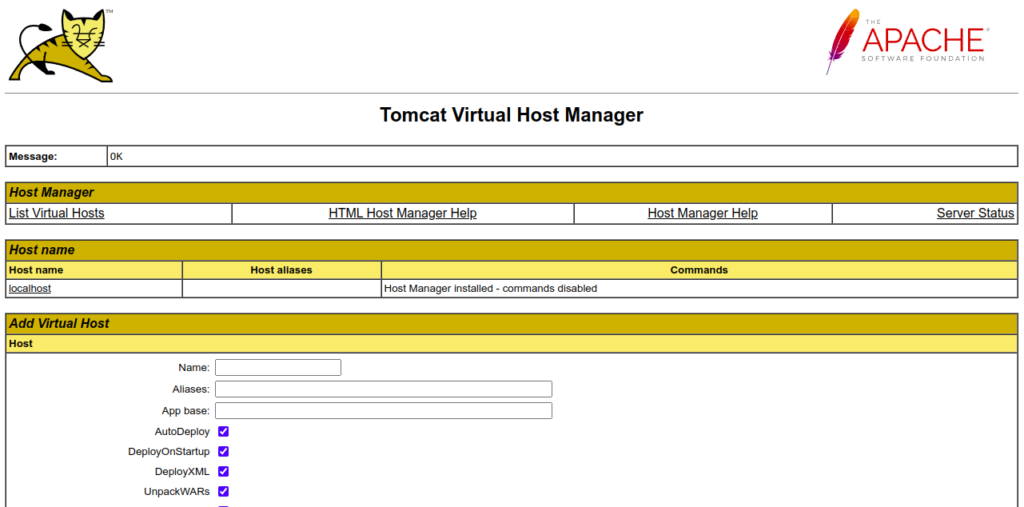
To access the Host Manager App, click on the Host Manager, you should see the following screen:
Conclusion
Congratulations! You have successfully installed Apache Tomcat 10 on Arch Linux. You can now deploy your Java application easily with Apache Tomcat. You can try Tomcat one of our dedicated server hosting from Atlantic.Net!