Zeek, formerly known as Bro, is a network security monitoring tool for Linux. It is a free, open-source, and flexible tool that sits on a “sensor,” or cloud platform, and observes network traffic. Zeek monitors and records connections, the volume of packets sent and received, attributes about TCP sessions, and other metadata that is useful for analyzing network behavior. It helps you trace complex events across multiple flows and protocols with ease.
In this post, we will show you how to install the Zeek network security monitoring tool on Ubuntu 20.04.
Step 1 – Install Zeek
By default, Zeek is not included in the Ubuntu default repository, so you will first add the Zeek repository to your system. Install all required dependencies with the following command:
apt-get update -y apt-get install curl gnupg2 wget -y
Next, download and add the Zeek GPG key using the following command:
curl -fsSL https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/security:zeek/xUbuntu_20.04/Release.key | gpg --dearmor | tee /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/security_zeek.gpg
Next, add the Zeek repository to APT with the following command:
echo 'deb http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/security:/zeek/xUbuntu_20.04/ /' | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/security:zeek.list
Finally, update the repository cache and install the Zeek with the following command:
apt-get update -y apt-get install zeek -y
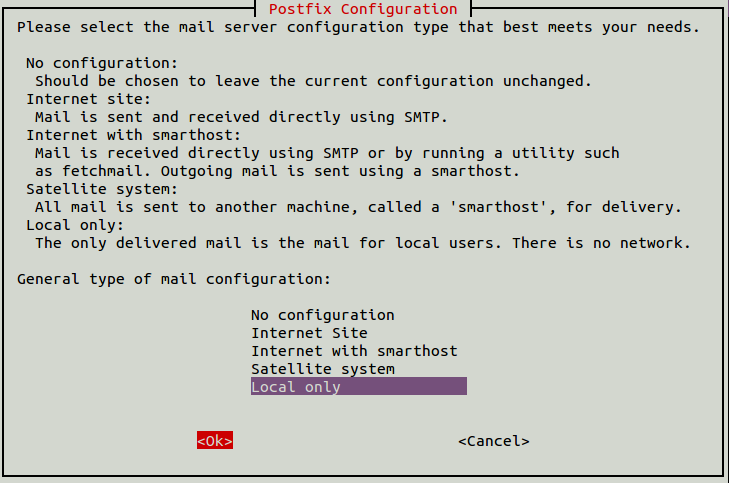
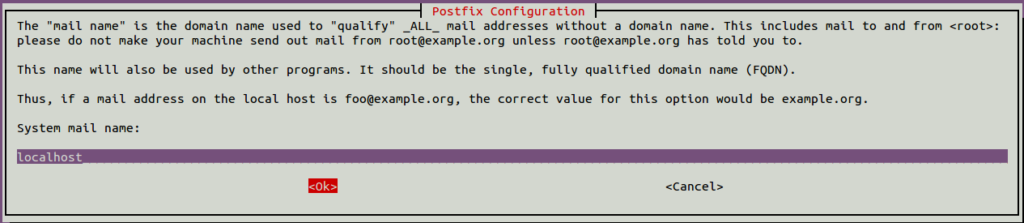
During the installation, you will be asked to provide some postfix settings as shown below:
After installing Zeek, you will need to add Zeek to the system path. You can do it with the following command:
echo "export PATH=$PATH:/opt/zeek/bin" >> ~/.bashrc
Next, activate ~/.bashrc with the following command:
source ~/.bashrc
Now, verify the Zeek version with the following command:
zeek --version
You should get the following output:
zeek version 4.0.3
Step 2 – Define Your Network
Next, you will need to define the network that you want to monitor. You can define it by editing /opt/zeek/etc/networks.cfg file.
nano /opt/zeek/etc/networks.cfg
Here are the default values. You can add your own networks at the end of the file:
10.0.0.0/8 Private IP space 172.16.0.0/12 Private IP space 192.168.0.0/16 Private IP space
Save and close the file when you are finished.
Step 3 – Configure Zeek Cluster
By default, Zeek is configured to run in standalone mode. In this section, we will configure Zeek in cluster mode.
First, edit the Zeek main configuration file:
nano /opt/zeek/etc/node.cfg
Comment out the following lines:
#[zeek] #type=standalone #host=localhost #interface=eth0
Add the following lines at the end of the file.
[zeek-logger] type=logger host=your-server-ip # [zeek-manager] type=manager host=your-server-ip # [zeek-proxy] type=proxy host=your-server-ip # [zeek-worker] type=worker host=your-server-ip interface=eth0 # [zeek-worker-lo] type=worker host=localhost interface=lo
Save and close the file when you are finished, then check the configuration file for any errors with the following command:
zeekctl check
If everything is fine, you should get the following output:
zeek-logger scripts are ok. zeek-manager scripts are ok. zeek-proxy scripts are ok. zeek-worker scripts are ok. zeek-worker-lo scripts are ok.
Next, deploy the Zeek configuration with the following command:
zeekctl deploy
You should get the following output:
starting logger ... starting manager ... starting proxy ... starting workers ...
Step 4 – Verify Status of Zeek
You can now check the status of the Zeek instance using the following command:
zeekctl status
You should get the following output:
Name Type Host Status Pid Started zeek-logger logger your-server-ip running 10479 25 Jul 06:34:08 zeek-manager manager your-server-ip running 10529 25 Jul 06:34:10 zeek-proxy proxy your-server-ip running 10579 25 Jul 06:34:12 zeek-worker worker your-server-ip running 10648 25 Jul 06:34:14 zeek-worker-lo worker localhost running 10650 25 Jul 06:34:14
At this point, Zeek will start to analyze traffic as per the configuration file and write logs to the /opt/zeek/logs/current directory.
You can check all generated log files with the following command:
ls -l /opt/zeek/logs/current/
You should see the following output:
-rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 1780 Jul 25 06:36 broker.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 2346 Jul 25 06:36 cluster.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 578 Jul 25 06:36 conn.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 28733 Jul 25 06:36 loaded_scripts.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 596 Jul 25 06:36 ntp.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 187 Jul 25 06:36 packet_filter.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 601 Jul 25 06:36 stats.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 0 Jul 25 06:36 stderr.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 188 Jul 25 06:36 stdout.log -rw-r--r-- 1 root zeek 482 Jul 25 06:36 weird.log
Run the following command to check the connection logs.
tail /opt/zeek/logs/current/conn.log
Sample output:
1627194994.735281 Cu51ph1SpnaI5e8VGe 184.188.36.2 56921 your-server-ip 445 tcp - 0.000036 0 0 REJ F F 0 Sr 1 52 1 40 - 1627194997.416217 CEMJC91xoEHySwvNdg your-server-ip 47762 your-server-ip 47466 tcp - - - - OTH FF 0 CcCc 0 0 0 0 - 1627194998.422707 C9lEWO2Cka3rN7kafa your-server-ip 46316 your-server-ip 47761 tcp - - - - OTH FF 0 CcCc 0 0 0 0 - 1627195000.441681 Cw8Uy5wH7AyZlUxg your-server-ip 46310 your-server-ip 47761 tcp - - - - OTH FF 0 CcCc 0 0 0 0 -
Run the following command to check the cluster logs:
tail /opt/zeek/logs/current/cluster.log
Sample output:
1627194993.480149 zeek-proxy got hello from zeek-worker (37A494EB63B75E2A52F1EA47CA05933C608362F3#13744) 1627194993.506139 zeek-proxy got hello from zeek-worker-lo (78A849E99E95C3EB4A0E457797D42C13BAFF3E14#13742) 1627194993.506938 zeek-manager got hello from zeek-worker (37A494EB63B75E2A52F1EA47CA05933C608362F3#13744)
Step 5 – Check Zeek Node Processes
You can also check the processes running on each node.
To check the running processes of the zeek-manager node, run the following command:
zeekctl ps.zeek zeek-manager
You should get the following output:
USER PID PPID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TT S STARTED TIME COMMAND >>> your-server-ip (-) root 13574 13568 1.7 2.1 1263568 87912 ? S 06:36:26 00:00:01 zeek (+) root 13624 13618 1.5 2.2 642620 88836 ? S 06:36:27 00:00:01 zeek (-) root 13673 13667 1.3 2.1 640932 87224 ? S 06:36:29 00:00:01 zeek (-) root 13742 13732 2.1 5.4 771956 218288 ? S 06:36:31 00:00:01 zeek (-) root 13744 13731 2.2 5.4 772548 219764 ? S 06:36:31 00:00:02 zeek
Conclusion
In this post, you learned how to install and configure the Zeek network security monitoring tool on Ubuntu 20.04. For more information on Zeek configuration, visit the Zeek documentation. Get started with Zeek today on dedicated server hosting from Atlantic.Net!