What is VMware?
VMware is a software company that specializes in virtualization and cloud computing. It provides an alternative to dedicated hosts. In 2024, VMware was acquired by Broadcom, raising questions about the future of its products and uncertainty about future licensing costs. This has led many organizations to consider alternatives such as Nutanix.
VMware's solution categories include:
- Virtualization: Creates a software layer that allows a computer's hardware to be divided into multiple virtual machines (VMs). Each VM can run its own operating system and act like a separate computer.
- Networking: Simplifies application delivery and automates operations with network virtualization and load balancing.
- Cloud infrastructure: Deploys private cloud infrastructure solutions.
- Software-defined data center (SDDC): Virtualizes almost every computing function into a software-defined data center.
- Storage software: Allows IT departments to place application workloads on the most cost-effective compute resource.
VMware's main products include:
- VMware vSphere
- VMware ESXi
- VMware vCloud
- VMware Hyper Converged Infrastructure (HCI)
- VMware Horizon
- VMware Fusion
- VMware Workstation
- VMware Player
- VMware ThinApp
- VMware Cloud Management Services
VMware has a large and loyal user base, but also has its critics. Some say that VMware has a very deep product lineup, and its software is mature and battle-tested. Others say that VMware is complex, has fewer compatibility options and costly licensing fees.
VMware vSphere
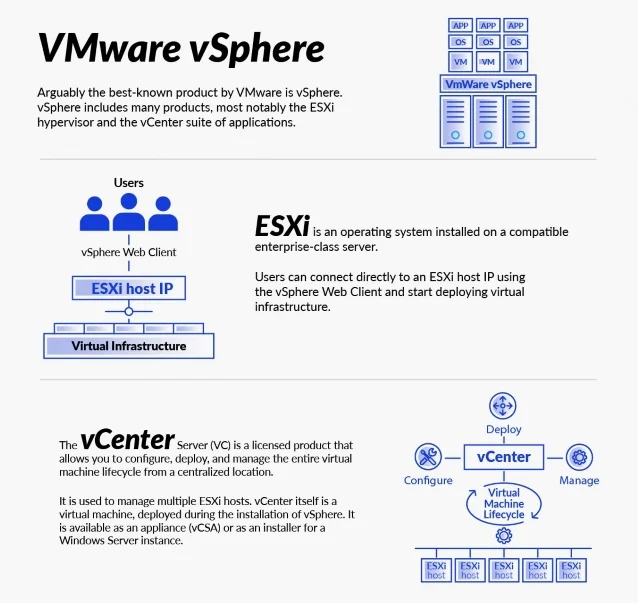
Arguably the best-known product by VMware is vSphere. vSphere includes many products, most notably the ESXi hypervisor and the vCenter suite of applications.
To use many of the licensed enterprise-class features of vSphere, such as cloning servers, vMotion, high availability and DRS, this requires a vCenter server.
The vCenter Server (VC) is a licensed product that allows you to configure,
deploy, and manage the entire virtual machine lifecycle from a centralized
location. It is used to manage multiple ESXi hosts.
Each virtual environment requires at least 1 vCenter server. Once installed, vCenter can be accessed via a web GUI and can manage the entire connected virtualized estate. It is used to simplify management of VMs, complete daily admin tasks, and complete virtualized infrastructure management. vCenter provides access to all the connected clusters, hosts, networking, and storage from one easy-to-manage web interface. For a developer, VMware PowerCLI can be used to automate management of vSphere.
VMware ESXi
ESXi is an operating system installed on a compatible enterprise-class server. ESXi is powered by the VMKernel, which manages the virtual machines allowing them to be created and interacted with. The VMKernel directly manages the host I/O between allocated resources and the virtual machines.
Users can connect directly to an ESXi host IP using the vSphere Web Client and start deploying virtual infrastructure. Managing a single host is acceptable in a lab environment; however, in an enterprise environment, multiple hosts are used with numerous storage and networking components.
VMware vCloud
The VMware vCloud suite is a software-defined datacenter solution based on a vSphere private cloud implementation. It has evolved from vSphere due to the changing demands of Cloud / IT managed service providers. It offers a full cloud solution with datacenter virtualization, automated operations (VMware Aria), high availability, resilient infrastructure, and, more recently, infrastructure delivery automation (vSAN / NSX).
VMware vCloud includes several key features. It uses vSphere for computing and VMware Aria Automation for a policy-defined compute automation, for example, creating a policy-driven automated host deployment. vRealize Operations manager is also included; this is a capacity management suite and licensing manager used to monitor the entire virtual infrastructure and predict future capacity requirements.
A typical vCloud Cloud Management setup consists of at least 2 sites. Each site is connected by a dark fiber, and each has multiple hosts and replicated storage. vCloud includes the VMware vCenter Site Recovery Manager (SRM), a high availability disaster recovery solution which replicates data between sites. In the event of a disaster, SRM will use predefined policies to failover servers and services from Site A to Site B. It is an automated process and enables managed service providers to offer 99.99% (always online) uptime capability.
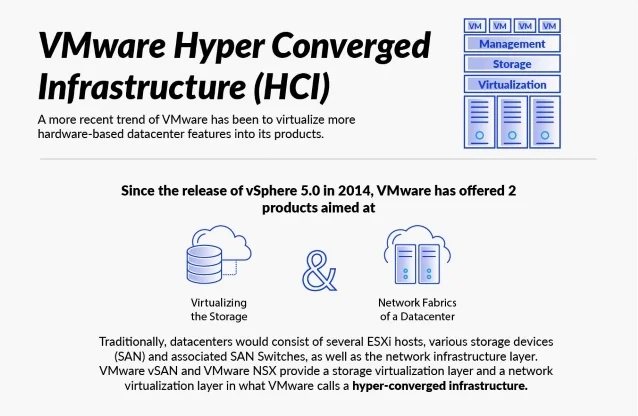
VMware Hyper Converged Infrastructure (HCI)
A more recent trend of VMware has been to virtualize more hardware-based datacenter features into its products. Since the release of vSphere 5.0 in 2014, VMware has offered 2 products aimed at virtualizing the storage and network fabrics of a datacenter. Traditionally, datacenters would consist of several ESXi hosts, various storage devices (SAN) and associated SAN Switches, as well as the network infrastructure layer. VMware vSAN and VMware NSX provide a storage virtualization layer and a network virtualization layer in what VMware calls a hyper-converged infrastructure.
vSAN is a software-defined enterprise-class storage solution. vSAN can use any typical server storage as part of a larger virtual storage device. vSAN then applies deduplication and compression to the data to minimize the VM footprint, which in turn can provide better performance than traditional storage infrastructure can. There is no need for a dedicated storage SME, as all policy creation and storage management is done in vCenter. vSAN can be scaled up simply by adding more storage to the provisioned vSAN Hosts.
VMware has also recently introduced NSX, which provides virtualization of the entire network fabric. It provides a secure, agile virtual network which is managed by vCenter. NSX can virtualize the role of any firewall, switch, router or load balancer. Network policies can be applied per server, allowing you to isolate infrastructure to different parts of the network, thus improving overall network security. NSX network templates can be deployed instantly, enabling professionals to build network infrastructure from their workspace in a few clicks.
VMware Horizon
The software discussed so far is typically used for datacenter-based infrastructure services, but VMware also has a large presence in the desktop workspace. VMware Horizon is the VMware virtual desktop environment (VDI), which allows desktop and applications to be delivered directly to the user on any type of workstation. This is commonly used within organizations to provide employees access to a centralized and identity-controlled application stack.
VMware Workstation
VMware Workstation is a desktop virtualization software that enables users to run multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single Windows or Linux PC. It is intended for professionals such as developers, testers, and IT administrators who need to create, test, and deploy software across various platforms. Workstation offers advanced features including support for the latest hardware, robust networking capabilities, integration with VMware vSphere, and comprehensive snapshots for easy rollback.
VMware Fusion
VMware Fusion is intended for Mac users, providing the capability to run Windows, Linux, and other operating systems alongside macOS without rebooting. Fusion is popular among developers and IT professionals who need to test applications across different OS environments. It offers advanced features like integration with VMware vSphere, support for DirectX 11, and a simplified user interface. Fusion also supports the latest macOS features, making it a useful tool for creating and managing virtual machines on Mac hardware.
VMware Player
VMware Player, also known as VMware Workstation Player, is a free, simplified version of VMware Workstation aimed at home users and students. It allows users to create and run virtual machines on a Windows or Linux PC. VMware Player supports basic virtualization needs with the ability to run restricted VMs created by VMware Workstation or VMware Fusion Pro. It’s a suitable tool for users who need to run multiple operating systems on a single PC without advanced management features.
VMware ThinApp
VMware ThinApp is an application virtualization solution that packages applications into self-contained executable files. This allows applications to be run without installation, providing compatibility across different versions of Windows and reducing conflicts with other software. ThinApp simplifies application deployment and management, enabling IT administrators to deliver, update, and manage applications more efficiently. It also enhances security by isolating applications from the underlying operating system and other applications
VMware Cloud Services
The VMware cloud is the offering from VMware for cloud-based infrastructure services. It is heavily integrated with Amazon Web Services (AWS) and offers the user a cloud-based service of many of the popular VMware applications discussed here. This eliminates the requirement for local datacenter services and the cost associated with it, and enables many individuals or companies to leverage VMware products for their personal use. Many businesses are moving toward the cloud as part of their future IT strategy.
VMware Pros and Cons
When evaluating whether to use VMware, organizations should consider the following advantages and disadvantages.
VMWare Pros
- Established market presence: VMware has been a leading provider in virtualization and cloud infrastructure for over two decades. Its extensive experience and innovation have given it a reputation as a reliable and advanced solution provider.
- Maturity and robustness: VMware's products are known for their stability and reliability. Years of development and real-world testing have resulted in a mature product lineup that can handle demanding enterprise environments.
- Integration with legacy systems: VMware solutions offer strong compatibility and integration with existing legacy systems, enabling organizations to modernize their IT infrastructure without the need for a complete overhaul.
- Comprehensive management tools: VMware provides an extensive suite of management tools that simplify the administration of virtual environments. Tools like vCenter Server and VMware PowerCLI offer centralized control and automation capabilities, making it easier to manage large-scale deployments.
VMWare Cons
- Complex infrastructure: VMware solutions can be complex to set up and manage, often requiring specialized knowledge and skills. This complexity can increase the time and effort needed for deployment and ongoing management.
- Limited compatibility options: While VMware offers integration with many systems, it has fewer compatibility options compared to some of its competitors. This limitation can restrict the flexibility organizations have when choosing hardware and software components.
- Costly scalability: Scaling VMware environments can be expensive due to the licensing costs associated with its products. As organizations grow their virtual infrastructure, the incremental costs can become a financial burden.
- Inflexible licensing: VMware's licensing model can be inflexible, often requiring long-term commitments and offering limited options for customization. This can be a disadvantage for organizations that need more adaptable licensing solutions.
- High license costs: The cost of VMware licenses is generally higher compared to some alternative solutions. These high costs can be a deterrent for smaller organizations or those with limited budgets.
- Uncertainty due to Broadcom acquisition: The acquisition of VMware by Broadcom has introduced uncertainty regarding the future direction of VMware's product offerings and pricing models. This can make it difficult for organizations to plan their long-term IT strategies.
