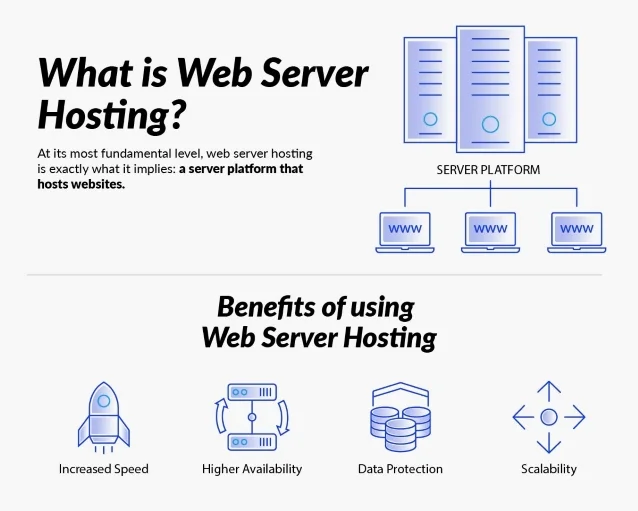
What is Web Server Hosting?
At its most fundamental level, web server hosting is exactly what it implies: a server platform that hosts websites. A web server handles the HTTP requests when end-users seek out web pages. The web server does not necessarily host all the files that an HTTP request is calling for from each website, but it acts as the facilitator to acquire those files to make the request happen as quickly as possible. For most websites' owners, utilizing a host can be both economically wise and convenient, as the host also provides space for hundreds or even thousands of other websites employing similar resources.
Web Server Applications: Apache, IIS, and NGINX
Web server applications help the server support HTTP requests. There are several web server applications available today, both commercial and open source. Three of the most popular are the Apache HTTP web server, the Microsoft IIS Web Server and the NGINX web application platform.
Apache HTTP web server is an open source web application created by the Apache Software Foundation and available free with support from the Apache open source community. Commercial support is provided by managed service providers. Because Apache is a modular application, it works natively with applications such as MySQL, Tomcat, and PHP. Apache powers a large percentage of the internet websites and can be scaled to handle high volumes of traffic on minimal hardware. Apache is popular with the Linux community and is trusted by some of the biggest companies online.
Microsoft IIS (Internet Information Services) server is a licensed web server application and an installable role bundled with all Microsoft Windows Server products. Technical support is provided by dedicated managed service providers, and MSPs have direct access to Microsoft technical support channels. IIS easily integrates with existing Microsoft products, such as Office, SharePoint, and PowerShell. IIS is incredibly popular with enterprises due to its user-friendly design and ability to delegate control to different support teams.
NGINX is a little different from IIS and Apache; not only is NGINX an HTTP web server, but it is also a reverse proxy (front end), a proxy mail server (POP3/IMAP/SMTP) and a generic TCP/UDP proxy server for load balancing. NGINX is an open source application that is incredibly well optimised, allowing it to scale well for heavy workloads. The additional services offered by NGINX are popular with web developers, as NGINX offers a full suite of applications to run a website from a single server. You can even combine NGINX and Apache on a single server. NGINX can be used as a proxy to an Apache web server, giving developers the flexibility of both web servers.
Benefits of using Web Server Hosting
Increased Speed - For nearly all web hosting situations, faster websites are better websites. Generally, the faster a website loads, the more sales and conversions the site will generate. End-users are notoriously impatient with slow-loading sites; according to Retail Dive, every second of additional loading time results in a 7% drop in conversion rate. And don’t forget that Google uses loading speed as a variable in its search rankings.
Higher Availability - In the digital world, availability refers to the amount of time required to respond to a request made by an end-user. Achieving high availability involves eliminating single points of failure. Higher availability means better reliability and tougher security and also lowers the risk of a website crashing.
Data Protection Up-to-date security technology is a must in web server hosting. That includes data centers that are state-of-the-art, with airtight security to keep watch of clients’ most sensitive data. Most web server hosts will custom-build their data centers for specific client purposes and have security watching them 24/7/365 to ensure they stay secure.
Scalability One of the most buzzworthy words of the past decade, scalability, is all about letting a business, technology, or service grow bigger (or become smaller) as the need arises. If your company is running its own web server, growth means extra costs of buying new hardware and configuring it properly. When your organization’s web server is hosted by a world-class data center, growing to match demand is as simple as sending an email or making a quick phone call.
Dedicated Servers vs. Cloud Hosting
There are two environments where a website can be hosted - a dedicated physical server or a cloud server. Both have their strengths and weaknesses depending on an organization’s specific needs. Below is a breakdown of each environment, along with a deeper dive into its individual strengths and weaknesses.
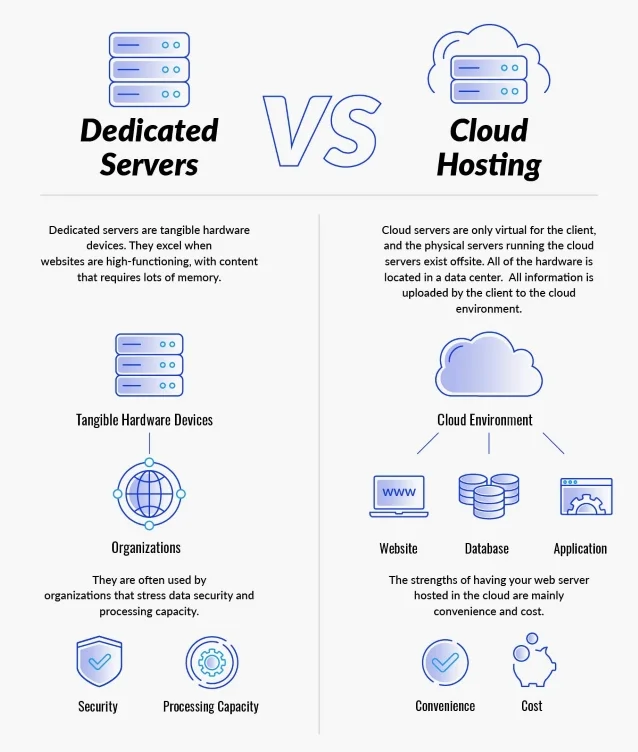
Dedicated servers: Dedicated serversare tangible hardware devices. They are often used by organizations that stress data security and processing capacity. Dedicated servers are tangible hardware devices. They are often used by organizations that stress data security and processing capacity. They excel when websites are high-functioning, with content that requires lots of memory. For instance, a company that makes tractors might have multiple videos of every vehicle posted online, along with tech specs and a treasure trove of proprietary data on various components, upgrades, etc. Keeping that information on a physical, in-house server makes more sense than putting it in the cloud. The end-users’ requests to play hundreds of videos means that a dedicated server makes sense. On the downside, as with most physical hardware, technology tends to get outdated quickly, which leads to higher capital expenses in replacing equipment, performing maintenance or upgrading via patches, etc.
The same is true for scaling up or down. More memory must be added, or perhaps entirely new hardware purchased, to handle the increased flow of traffic.
Cloud-hosted servers: Cloud servers are only virtual for the client, and the physical servers running the cloud servers exist offsite. All of the hardware is located in a data center. All information is uploaded by the client to the cloud environment, whether it’s a website, database, application, or something else. The strengths of having your web server hosted in the cloud are mainly convenience and cost. For starters, the economies of scale will mean your firm pays far less for memory space and processing power than it would with a dedicated server, since most websites don’t demand enormous consumption of either. Your firm is paying for exactly the amount of space it needs - no more, no less.
If your firm has a definitive busy season, a definitive slow season, or both, you can also easily scale your needs up or down as demand requires, saving money and time.
The biggest negative for cloud-hosted servers is that data may exist on a shared physical server that is running multiple virtual servers. Firms which inherently deal with risky data or that must adhere to strict compliance regulations on how they store and move data often may worry that the cloud not secure or advanced enough for their purposes and should seek out a cloud provider that makes security a priority, or private cloud hosting.
Award-Winning Hosting Solutions & Services
Simple, Fast, Reliable Server Hosting
Share Your Vision With Us
And We Will Develop a Hosting Environment Tailored to Your Needs!
Contact an advisor at 866-618-DATA (3282), email [email protected], or fill out the form below.
Don't just take our word for it: Cyber Defense Magazine recognized Atlantic.Net as "Most Innovative Cloud Hosting Provider" in the 2024 Global Infosec Awards.