Mission-critical enterprise data resources need to be readily available to allow organizations to meet their business objectives. The storage devices employed to furnish users and applications with access to this valuable data must exhibit elevated levels of performance and resiliency. One way to keep data flowing is to protect it by storing it in RAID arrays.
RAID stands for redundant array of independent disks. It is a storage methodology that uses multiple hardware devices and techniques to ensure data remains available if one or several array components fail.
This article looks at how the variety of RAID implementations offer businesses various levels of data protection and performance. We also discuss issues that can arise with RAID arrays and present reasons that effective monitoring should be in place.
How RAID Arrays Are Constructed
RAID arrays are built using a combination of up to three fundamental data storage concepts. As we will see shortly, different RAID levels are constructed using these concepts to provide varying levels of performance and data protection.
Disk Mirroring
In disk mirroring, data is written simultaneously to multiple disks. Mirroring offers protection against hardware failure by making the same data available on several physical devices.
If a mirrored disk fails, performance is maintained by immediately switching to an alternate device. Mirroring eliminates the time required to restore a disk and reconstruct a file system if a non-mirrored storage device fails. Resiliency and redundancy are provided by mirrored disks which make them an appropriate choice for storing business-critical data.
Disk Striping
Disk striping is a technique that also uses multiple physical devices to augment the functionality of a single unit. When disk striping is implemented, multiple physical disks are treated as a single logical device. Blocks of data are segmented and stored across logically connected storage devices. Disk striping provides both advantages and disadvantages regarding data availability and performance.
The benefits of disk striping include:
- Simplified resource management as multiple physical disks are seen as a unified logical entity.
- Multithreading read and write requests across multiple disks improves performance.
A disadvantage that can affect storage systems employing disk striping is its fragility. When a disk fails, it can be impossible to get to the data stored on other disks where data was written. The potential exists for data to be lost if there is no hot-swapping ability built into the environment.
Parity
The use of parity checks is the third possible component of a RAID implementation. When parity checking is in play, a parity block is added to each byte of data. Parity bits are checked to ensure data accuracy and can be used to reconstruct data from failed drives. Parity error checking involves comparing data from different locations and can adversely affect I/O performance.
What Do Different RAID Levels Provide?
Various combinations of mirroring, striping, and parity checking are used in the implementation of different RAID levels. Understanding the differences between the levels is key to making the best choice for your business from the options available from your cloud service provider.
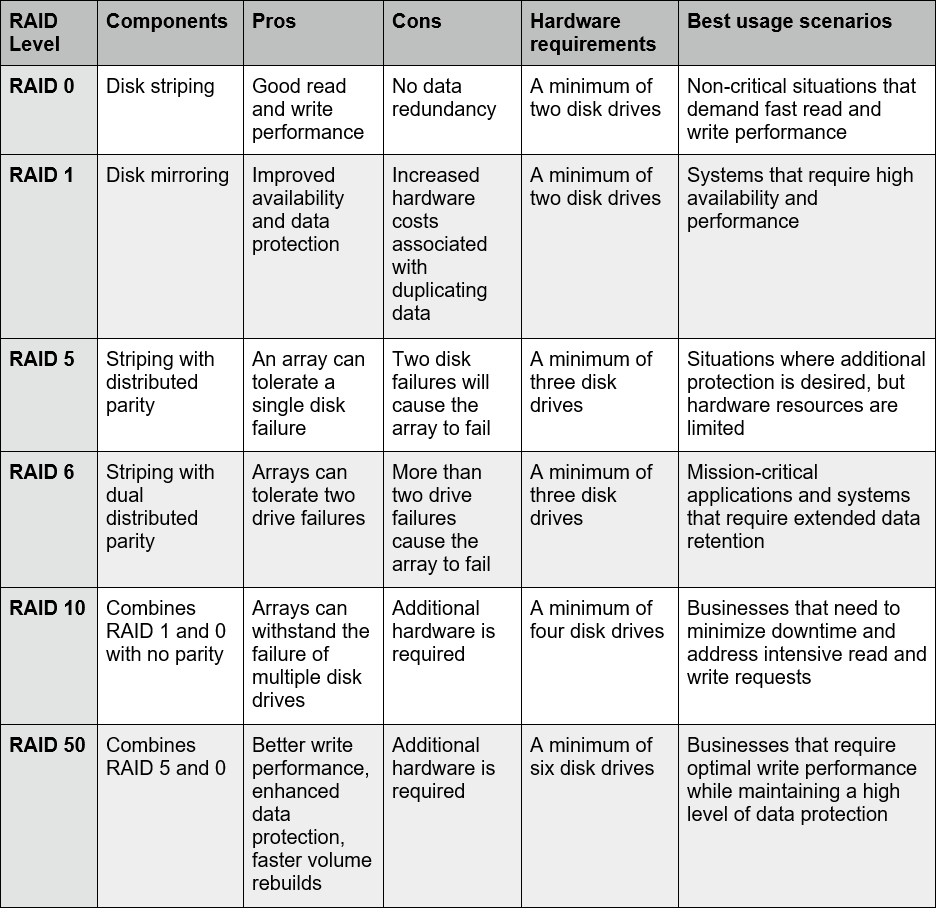
The following table summarizes the features and requirements of the most commonly implemented RAID levels.
Problems Affecting RAID Arrays
A RAID array can partially or completely fail due to a variety of reasons. A failed array should not be used until the problems are resolved to prevent further damage or data loss. The following are the most common reasons for the failure of a RAID array.
- Multiple disk failures – An array will fail if too many disks fail concurrently. While arrays can be run in degraded mode when experiencing a failed disk, this practice is not recommended as it can result in a total failure of the array.
- Failed RAID controller – All array operations are directed by the RAID controller. Power surges or other types of problems can cause the controller to fail. The array can experience multiple performance problems and may become inaccessible.
- Infrastructure issues – If the server hosting the RAID array crashes, the storage system can become inaccessible.
- Faulty volume rebuilds – An incorrectly rebuilt RAID volume can lead to degraded data access or a complete failure of the array.
Drive failures should be addressed and resolved as soon as possible. Letting an array continue to function at a degraded capacity opens the door for further problems and will increase the time necessary to repair the system. A large and complex RAID array that has experienced a failure can take an extended amount of time to rebuild.
Monitoring RAID Arrays
Unmonitored RAID arrays can be afflicted by degraded performance and potential data loss. Monitoring can be done using proprietary software supplied by the array’s hardware manufacturers. It can also be accomplished with general infrastructure monitoring tools that provide the necessary visibility into the array’s components of physical and logical disks.
When RAID arrays are implemented in-house, an organization’s storage team is usually responsible for monitoring the system. Based on the type of server you obtain from a cloud provider, the vendor may handle monitoring the array and making sure your data is safe and accessible.
Atlantic.Net’s RAID Offerings
Atlantic.Net has several different RAID implementations available for customers using their dedicated or VPS hosting offerings.
Customers who select a VPS solution have a highly redundant RAID 10 storage architecture protecting their data and ensuring high performance. The system keeps a business running by tolerating the failure of individual components while maintaining performance and data availability.
Choosing to deploy a dedicated server enables customers to choose from these storage options:
- SATA SSD RAID1;
- SATA SSD RAID10;
- NVMe SSD RAID10;
- A fully customizable implementation that provides any RAID level the customer desires.
Whichever hosting option your company chooses, its data will be well-protected and always available when needed with the RAID options available from Atlantic.Net.