LAMP stands for “Linux, Apache, MariaDB, and PHP,” a free, open-source, widely used software stack to host web applications. LAMP is a collection of free software solutions that are used together to enable a server to host dynamic websites and web applications. Each component of the LAMP stack contributes essential capabilities. Linux is a free and open-source operating system, Apache is an open-source web server that processes requests and serves web pages, MySQL is an open-source relational database management system for storing application data, and PHP is an open-source scripting language that works with Apache to help you create dynamic web pages.
In this post, we will explain how to install the LAMP stack on Oracle Linux 10.
Step 1 – Install Apache Web Server on Oracle Linux 10
By default, the Apache webserver is available in the Oracle Linux 10 default repo. You can install it by running the following command:
dnf install httpd -y
Once the Apache web server is installed, start the Apache service and enable it to start at system reboot.
systemctl start httpd systemctl enable httpd
Next, check the running status of the Apache service using the following command:
systemctl status httpd
You should see the following output:
● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Tue 2025-12-31 06:01:07 EDT; 7s ago
Docs: man:httpd.service(8)
Main PID: 1689 (httpd)
Status: "Started, listening on: port 80"
Tasks: 213 (limit: 23694)
Memory: 25.1M
CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service
├─1689 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─1690 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─1691 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
├─1692 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
└─1693 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND
Next, open your web browser and verify the Apache test page using the URL http://your-server-ip. You should see the Apache test page on the following screen:
Also Read
How to Install and Configure Apache Web Server on Oracle Linux 8
Step 2 – Install MariaDB Database Server on Oracle Linux 10
By default, the MariaDB or MySQL package is included on the Oracle Linux default repo. I would recommend installing a MariaDB server due to its numerous enhancements like high-performance storage engines and backward compatibility with MySQL.
You can install the MariaDB server with the following command:
dnf install mariadb-server -y
Once the MariaDB package is installed, start the MariaDB service and enable it to start at system reboot:
systemctl start mariadb systemctl enable mariadb
Next, verify the MariaDB service status using the following command:
systemctl status mariadb
Next, you will need to run the mysql_secure_installation script to secure the MariaDB installation.
You can run it using the following command:
mysql_secure_installation
You will then be prompted to set a MariaDB root password, remove anonymous users, disallow root login, and remove the test database as shown below:
Enter current password for root (enter for none): Set root password? [Y/n] Y New password: Re-enter new password: Remove anonymous users? [Y/n] Y Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n] Y Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n] Y Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n] Y
Step 3 – Install PHP on Oracle Linux 10
Next, you will need to install PHP (PHP Hypertext Preprocessor) in your system.
You can install PHP 8 with other extensions using the following command:
dnf install php php-fpm php-cli php-curl php-zip php-mysqli -y
Once PHP is installed, verify the installed version of PHP with the following command:
php -v
You should see the following command:
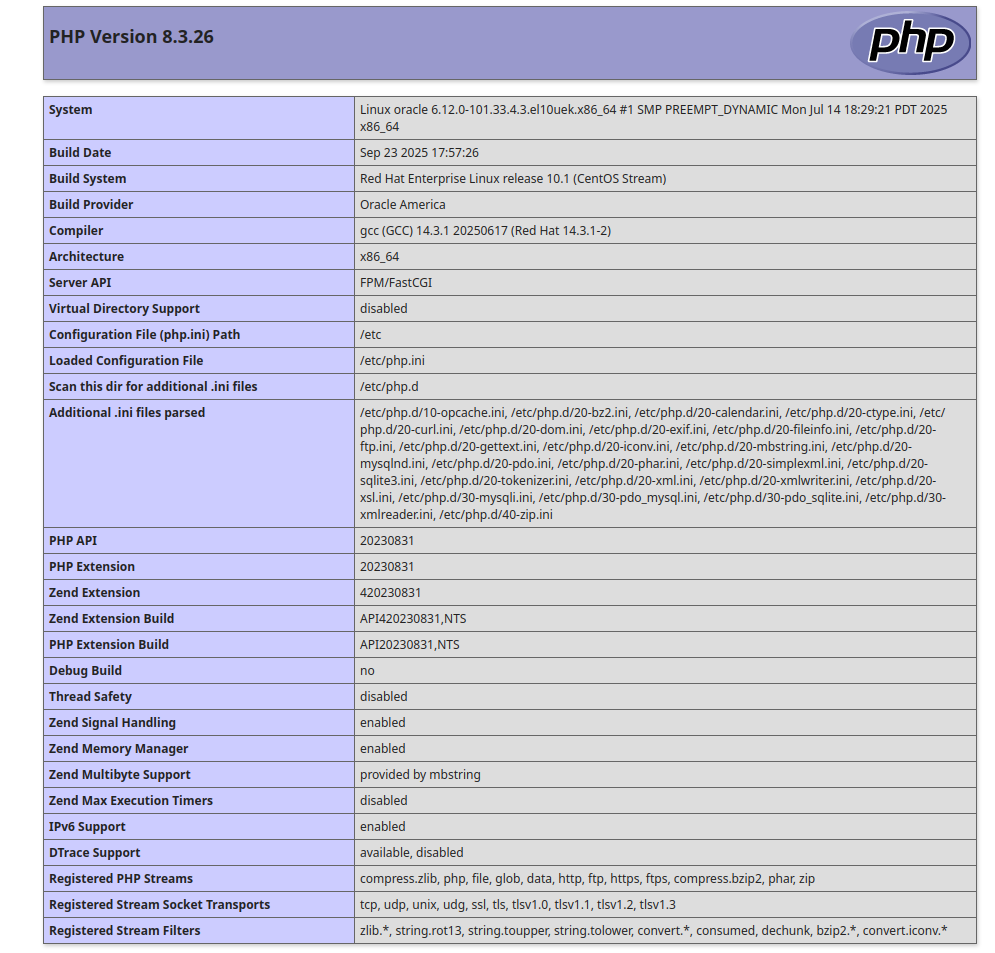
PHP 8.3.26 (cli) (built: Sep 23 2025 17:57:26) (NTS gcc x86_64) Copyright (c) The PHP Group Zend Engine v4.3.26, Copyright (c) Zend Technologies with Zend OPcache v8.3.26, Copyright (c), by Zend Technologies
You can also test the PHP version through the web browser.
To do so, create an info.php file:
nano /usr/share/httpd/noindex/info.php
Add the following code:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Save and close the file, then create a symlink of info.php.
ln -s /usr/share/httpd/noindex/info.php /var/www/html/info.php
Next, edit the Apache default configuration file:
nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/welcome.conf
Find the following line:
AllowOverride None
And replace it with the following line:
AllowOverride All
Next, restart the Apache and PHP-FPM service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart php-fpm httpd
Now, open your web browser and access the info.php page using the URL http://your-server-ip/info.php. You should see the PHP information on the following screen:
Also Read
Best Practice for Creating a HIPAA-Compliant LAMP Stack
Conclusion
In the above guide, we learned how to install the LAMP stack on Oracle Linux 10. You can now start developing a PHP-based web application and host it using the LAMP stack. Give it a try on your virtual private server from Atlantic.Net!