verified and Tested 05/20/15
Introduction
We will walk you through the LEMP install on your Fedora 22 Server in this How-To.
LEMP is simply a software bundle that consists of 4 components. L (Linux) is the platform’s core, which will sustain the other components. E(Nginx)will be used for the web service. M(MariaDB)will be used for database management, and P(PHP) will be the programming language, making the platform a LEMP.
Prerequisites
A cloud server with Fedora 22 already installed (which will take care of the L(Linux) aspect of the LEMP install). If you do not have a server, why not spin up a Fedora 22 server from Atlantic.Net in under 30 seconds?
Installing NGINX in Fedora 22
Install NGINX with the following command:
dnf install nginx
Start the NGINX service with the following command:
systemctl start nginx
Configure NGINX to start when the system is rebooted:
systemctl enable nginx
You will also need to add the following firewall rules to let HTTP and HTTPS ports through the local firewall. Run the following commands to add them to the firewall:
firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=public firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=https firewall-cmd --reload
You can then check the status of nginx by running:
systemctl status nginx
You will now have NGINX installed on your server and can be verified by typing in the following with your IP ADDRESS on your browser. Also, all configuration files are provided on the page.
If you do not know your IP address, you can use the following command to grab it:
ifconfig
You should get an output similar to this:
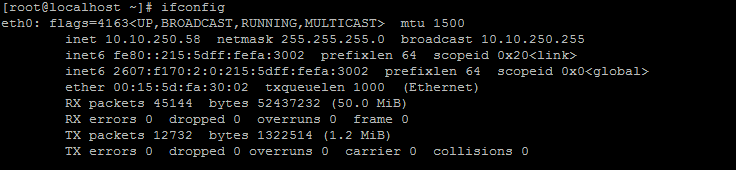
Using ifconfig to show ip address
In this server, our ip address shows 10.10.250.58, so we would put in our browser, http ://10.10.250.58 and get the following page:
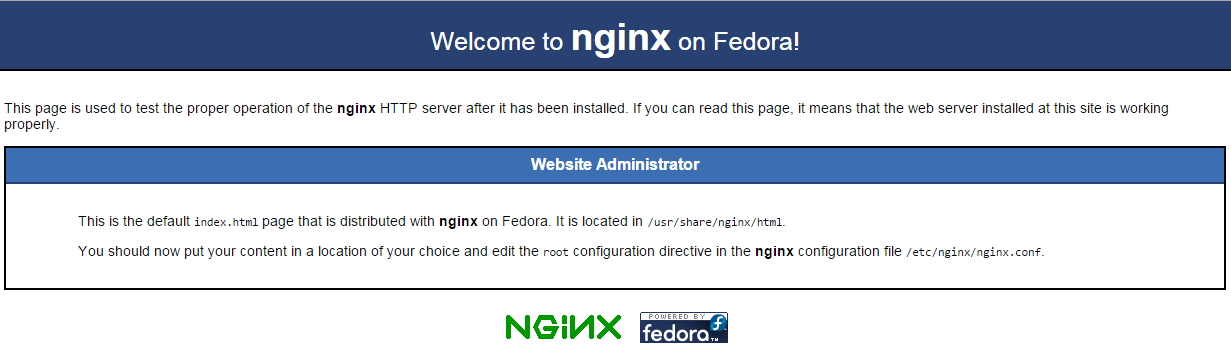
Nginx default page
Installing MariaDB on Fedora 22
Install MySQL with the following command to begin the install:
dnf install mariadb-server
Start the service with the following command
systemctl start mariadb
To have MariaDB start on boot, run the following command:
systemctl enable mariadb
You can then check the status of MariaDB to ensure it is running by using the command:
systemctl status mariadb
Set the MariaDB root password and secure MariaDB with the following command:
mysql_secure_installation
First, you will be prompted for the MariaDB root password. Since we installed MariaDB and did not set a root password, you would leave it blank and press Enter. You will then be asked if you would like to set the root password. Enter ‘Y’ for yes, and then create a password of your choice.
Note: Afterwards, you will be prompted with a series of questions. Type Y for yes on all of them. See the screenshot below:
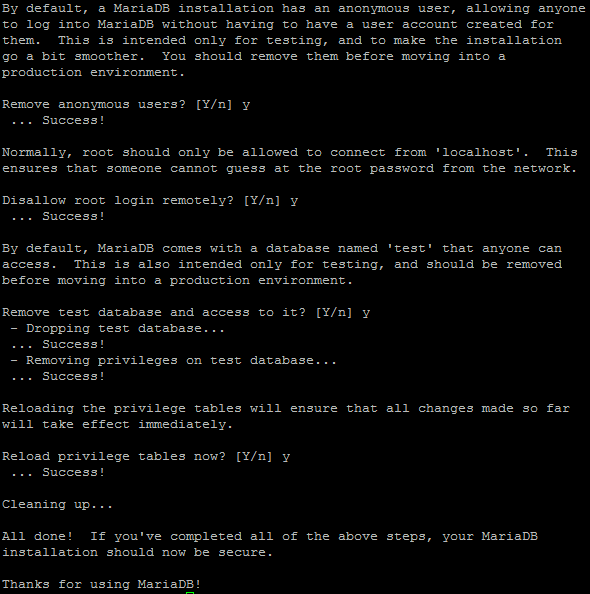
Series of questions to secure MariaDB
Installing PHP on Fedora 22
Install PHP with the following command to begin the install:
dnf install php php-mysql php-fpm
We will want to make a security configuration change in php.ini. Open php.ini with your text editor:
nano /etc/php.ini
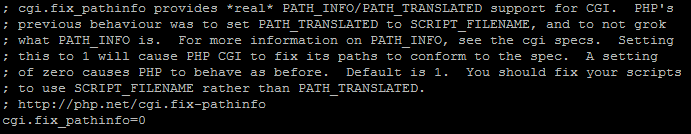
You will need to search for the following line; cgi.fix_pathinfo=1. Once there, delete the semi-colon and change the value from ‘1’ to ‘0’.
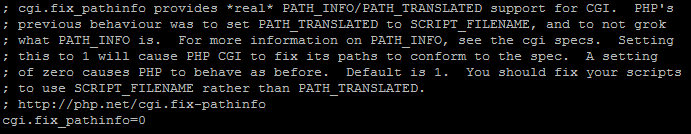
PHP.ini configuration file
This change will ensure you are not a victim of a well-known exploit in the Nginx environment. This changes how PHP files are interpreted.
Start php-fpm with the following command:
systemctl start php-fpm
To make sure it starts on boot, run the following:
PHP.ini configuration file
systemctl enable php-fpm
To check the status and make sure php-fpm is running:
systemctl status php-fpm
We will need to restart Nginx before testing PHP with all the configuration changes.
systemctl restart nginx
Now we are ready to test everything. We will create a simple PHP script to test it all. The path to adding the php script is located in the same place as the index.html we saw when installing Nginx. The path is /usr/share/nginx/html/ . We will open a new file under this path called test.php by running the following command.
nano /usr/share/nginx/html/test.php
Insert the following code in the space:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Save and exit.
In your browser, navigate to http :// ip.ad.dre.ss/test.php, and you will see information for your PHP installation.
PHP information page
Since you have tested PHP to be working, you will want to remove the test.php from your server, showing your PHP information publicly.
rm /usr/share/nginx/html/test.php
You can also view this detailed information of your PHP installation by running “php -i.”
Congratulations! You have just installed LEMP on your Fedora 22 Server. Check back with us for any new updates!
Learn more about our VPS hosting services and VPS hosting price.