Verified and Tested 04/02/2021
Introduction
In this How-To, we will walk you through the LEMP install on your CentOS 7 Server. LEMP is a software bundle that is made up of four parts (Linux, Nginx, MariaDB, and PHP). This how-to will be using CentOS 7 which was released on July 7th, 2014.

Installing EPEL and Remi in CentOS 7 for LEMP
In this how to we are going to install the Fedora epel release to quickly install Nginx and Remi for PHP using the following command:
sudo yum install epel-release sudo yum install http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm
Installing and Configuring NGINX in CentOS 7 for LEMP
Install NGINX with the following command:
sudo yum install nginx
Start the NGINX service with the following command:
sudo systemctl start nginx
Configure NGINX to start when the system is rebooted:
sudo systemctl enable nginx
You will now have NGINX installed on your server. This can be verified by typing in the following with your IP ADDRESS on your browser. Also, all configuration files are provided on the page.
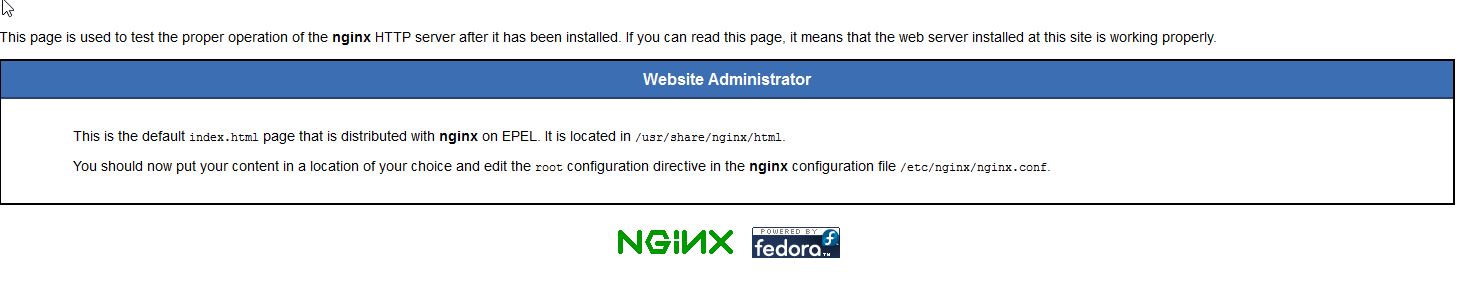
We can now verify Apache is working by opening your browser and entering the URL http://your-server's-address. you should get a blue Nginx test page similar to the image below.
Note: If you do not know your IP address, run the following command:
sudo ip addr show eth0
An example of running the command: ip addr show eth0 and getting 192.168.100.10 for the IP address.In our example we would put
http://192.168.100.10into our browser’s address bar.
Installing and Configuring MariaDB on CentOS 7 for LEMP
Install MariaDB with the following command to begin the install:
sudo yum install mariadb-server
Start the service with the following command:
sudo systemctl start mariadb
Set root MySQL password with the following command:
sudo /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation
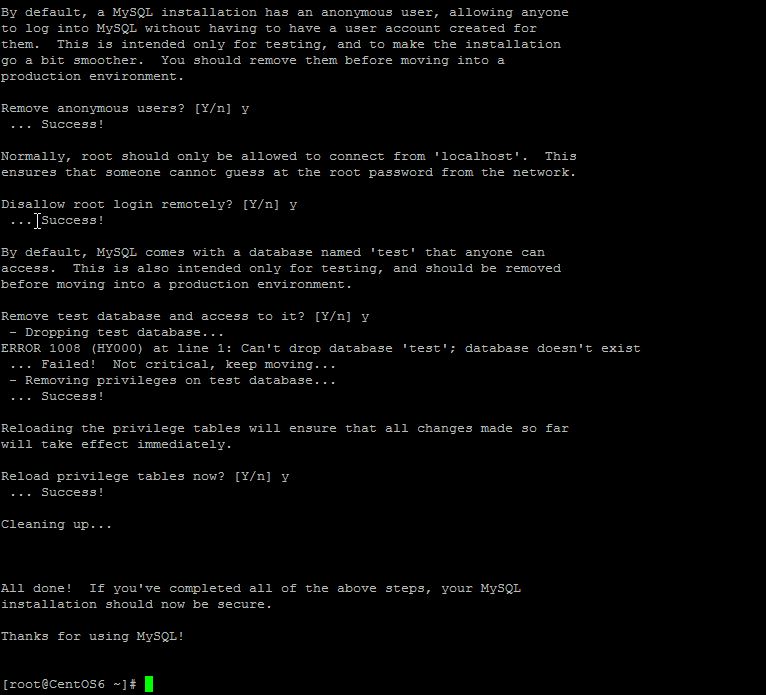
Note: You will be prompted with a series of questions. Just type Y for yes on all of them, see the screenshot below:
Sample my_secure_installation output.
Configure MariaDB to start when the system is rebooted:
sudo systemctl enable mariadb
Installing and Configuring php-fpm on CentOS 7 for LEMP
Install php-fpm with the following command:
sudo yum --enablerepo=remi-php74 install php-fpm php-mysql
Start the php-fpm service with the following command:
sudo systemctl start php-fpm
Make sure php-fpm starts on boot with the following command:
sudo systemctl enable php-fpm
Using your favourite editor, edit the file /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf and change user and group from apache to nginx. It should look similar to the block below.
; Unix user/group of processes ; Note: The user is mandatory. If the group is not set, the default user's group ; will be used. ; RPM: apache Choosed to be able to access some dir as httpd user = nginx ; RPM: Keep a group allowed to write in log dir. group = nginx
Now we need to make some changes to the Nginx configuration file so that php-fpm works correctly with Nginx. Using your favorite editor, edit the file /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf and carry out the following changes or copy the following block below into your conf file.
1) Add the index.php to the index location
2) Change the root location to /usr/share/nginx/html
3) Uncomment the Pass PHP scripts to FastCGI section.
4) Change the fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME to use /usr/share/nginx/html$fastcgi_script_name
#
# The default server
#
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name _;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
# Load configuration files for the default server block.
include /etc/nginx/default.d/*.conf;
location / {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
index index.php index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
location = /404.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
location ~ \.php$ {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /usr/share/nginx/html$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
Create a test PHP file in the following directory with the following command:
sudo vi /usr/share/nginx/html/info.php
Insert the following code in the space then save and exit:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
Restart apache so all the changes take effect:
sudo systemctl restart nginx
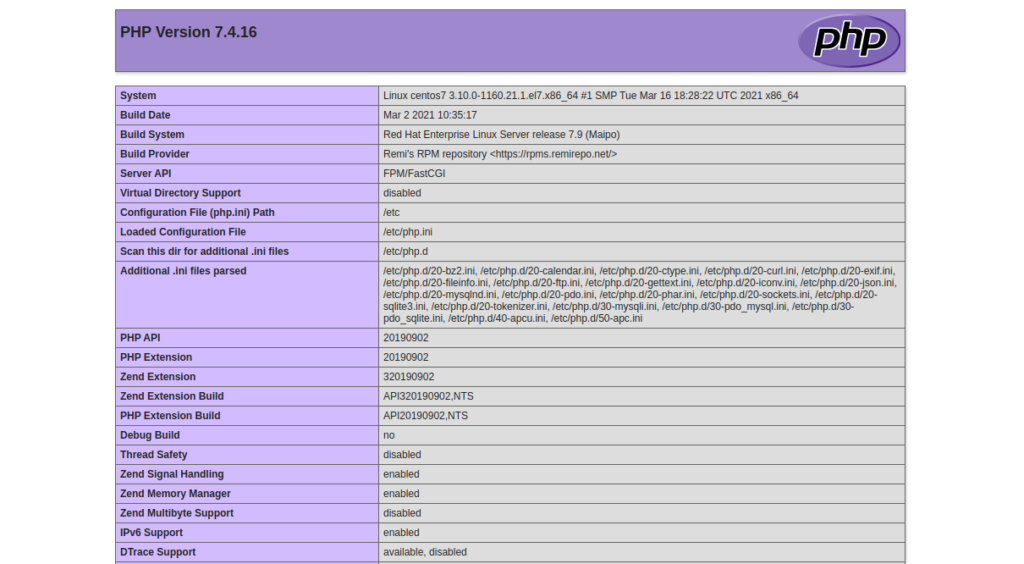
Test your page in your browser with the following hyperlink changed with yourIP address:
http://YOUR.IP.ADD.RESS/info.php
You should remove the info.php file as it could be used against you by an attacker. Delete it with the following command:
sudo rm /usr/share/nginx/html/info.php
Congratulations! You have just installed LEMP on your CentOS 7 Server. Thank you for following along in this How-To! Check back with us for any new updates and browse our scalable VPS hosting solutions for any sized business.