SonarQube is a free, open-source, self-managed code review tool that systematically helps you deliver clean code. It is a very useful quality analysis tool to scan source code for potential bugs and vulnerabilities and generates a report. SonarQube supports up to 30 programming languages and provides reports such as duplicate code, coding standards, code complexity, and security recommendation.
This post will show you how to install the SonarQube code analysis tool on Fedora.
Step 1 – Install Java OpenJDK
SonarQube is written in Java, so Java JDK must be installed on your server. If not installed, you can install it with the following command.
dnf install java-17-openjdk -y
Once Java is installed, you can verify the Java installation using the following command.
java --version
Output:
openjdk 17.0.3 2022-04-19 OpenJDK Runtime Environment 21.9 (build 17.0.3+7) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM 21.9 (build 17.0.3+7, mixed mode, sharing)
Step 2 – Install and Configure PostgreSQL Database
First, disable the default PostgreSQL repo and enable the PostgreSQL 14 repo.
dnf module reset postgresql -y dnf module enable postgresql:14
Next, install the PostgreSQL server with the following command.
dnf install postgresql-server postgresql
Next, initialize the PostgreSQL database using the following command.
postgresql-setup --initdb
Next, start the PostgreSQL service and enable it to start at system reboot.
systemctl enable --now postgresql
Next, log in to the PostgreSQL shell with the following command.
su - postgres psql
Next, create a database and user for SonarQube.
create user sonar; create database sonar owner sonar; grant all privileges on database sonar to sonar;
Next, set a password for the sonar user, then exit from the PostgreSQL shell.
ALTER USER sonar WITH ENCRYPTED password 'secure_password'; \q exit
Next, edit the PostgreSQL configuration file.
nano /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf
Find the following lines:
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 ident host all all ::1/128 ident
And, replace them with the following lines:
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 md5 host all all ::1/128 md5
Save and close the file, then reload the PostgreSQL service to implement the changes.
systemctl reload postgresql
Step 3 – Install and Configure SonarQube
First, create a dedicated user to run SonarQube.
useradd -M -d /opt/sonarqube/ -r -s /bin/bash sonar
Next, download the latest version of SonarQube.
wget https://binaries.sonarsource.com/Distribution/sonarqube/sonarqube-9.9.1.69595.zip
Next, unzip the SonarQube and move the unzipped directory to /opt
unzip sonarqube-9.9.1.69595.zip mv sonarqube-9.9.1.69595 /opt/sonarqube
Next, change the ownership of the SonarQube directory.
chown -R sonar:sonar /opt/sonarqube
Next, edit the SonarQube configuration file.
nano /opt/sonarqube/conf/sonar.properties
Define your database settings, host, port, Java options, and data directory.
sonar.jdbc.username=sonar sonar.jdbc.password=secure_password sonar.jdbc.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost/sonar ##How you will access SonarQube Web UI sonar.web.host=0.0.0.0 sonar.web.port=9000 ##Java options sonar.web.javaOpts=-Xmx512m -Xms128m -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError sonar.search.javaOpts=-Xmx512m -Xms512m -XX:MaxDirectMemorySize=256m -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError ##Also uncomment the following Elasticsearch storage paths sonar.path.data=data sonar.path.temp=temp
Save and close the file, then create a new wrapper.conf file and define your Java path.
nano /opt/sonarqube/conf/wrapper.conf
Add the following line.
wrapper.java.command=/usr/lib/jvm/jre-openjdk/bin/java
Save and close the file when you are done.
Step 4 – Create a Systemd Service File for SonarQube
Next, create a systemd file to manage the SonarQube service.
nano /etc/systemd/system/sonarqube.service
Add the following lines.
[Unit] Description=SonarQube service After=syslog.target network.target [Service] Type=forking ExecStart=/opt/sonarqube/bin/linux-x86-64/sonar.sh start ExecStop=/opt/sonarqube/bin/linux-x86-64/sonar.sh stop LimitNOFILE=65536 LimitNPROC=4096 User=sonar Group=sonar Restart=on-failure [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target
Save and close the file, then reload the systemd daemon to apply the changes.
systemctl daemon-reload
Next, start and enable the SonarQube service.
systemctl start sonarqube systemctl enable sonarqube
You can verify the SonarQube status using the following command.
systemctl status sonarqube
Output.
● sonarqube.service - SonarQube service
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/sonarqube.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2023-05-20 00:16:07 EDT; 4s ago
Process: 3092 ExecStart=/opt/sonarqube/bin/linux-x86-64/sonar.sh start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 3115 (java)
Tasks: 34 (limit: 4666)
Memory: 164.0M
CPU: 8.664s
CGroup: /system.slice/sonarqube.service
├─3115 java -Xms8m -Xmx32m --add-exports=java.base/jdk.internal.ref=ALL-UNNAMED --add-opens=java.base/java.lang=ALL-UNNAMED --add-opens=java.base/java.nio>
└─3140 /usr/lib/jvm/java-17-openjdk-17.0.3.0.7-1.fc34.x86_64/bin/java -XX:+UseG1GC -Djava.io.tmpdir=/opt/sonarqube/temp -XX:ErrorFile=/opt/sonarqube/logs/>
May 20 00:16:07 fedora systemd[1]: Starting SonarQube service...
May 20 00:16:07 fedora sonar.sh[3092]: /usr/bin/java
May 20 00:16:07 fedora sonar.sh[3092]: Starting SonarQube...
May 20 00:16:07 fedora sonar.sh[3092]: Started SonarQube.
May 20 00:16:07 fedora systemd[1]: Started SonarQube service.
Step 5 – Access SonarQube Web Dashboard
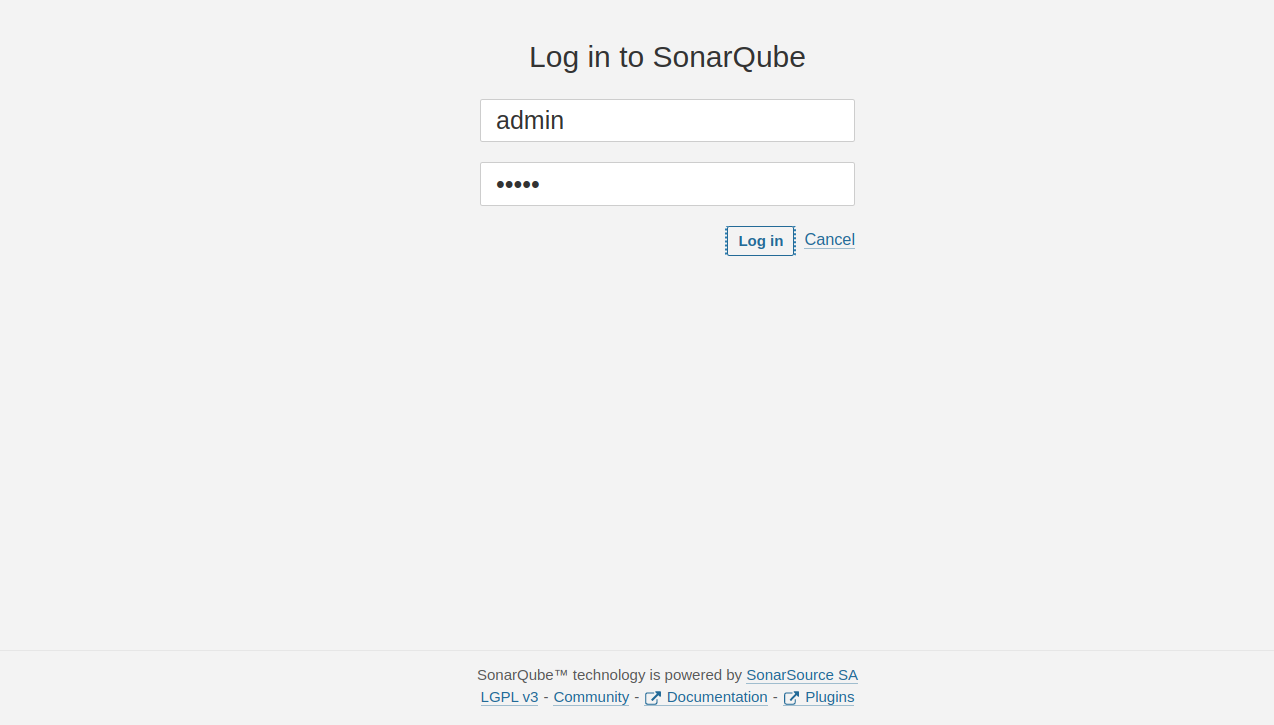
Now, open your web browser and access the SonarQube web UI using the URL http://server-ip:9000. You should see the SonarQube login screen.
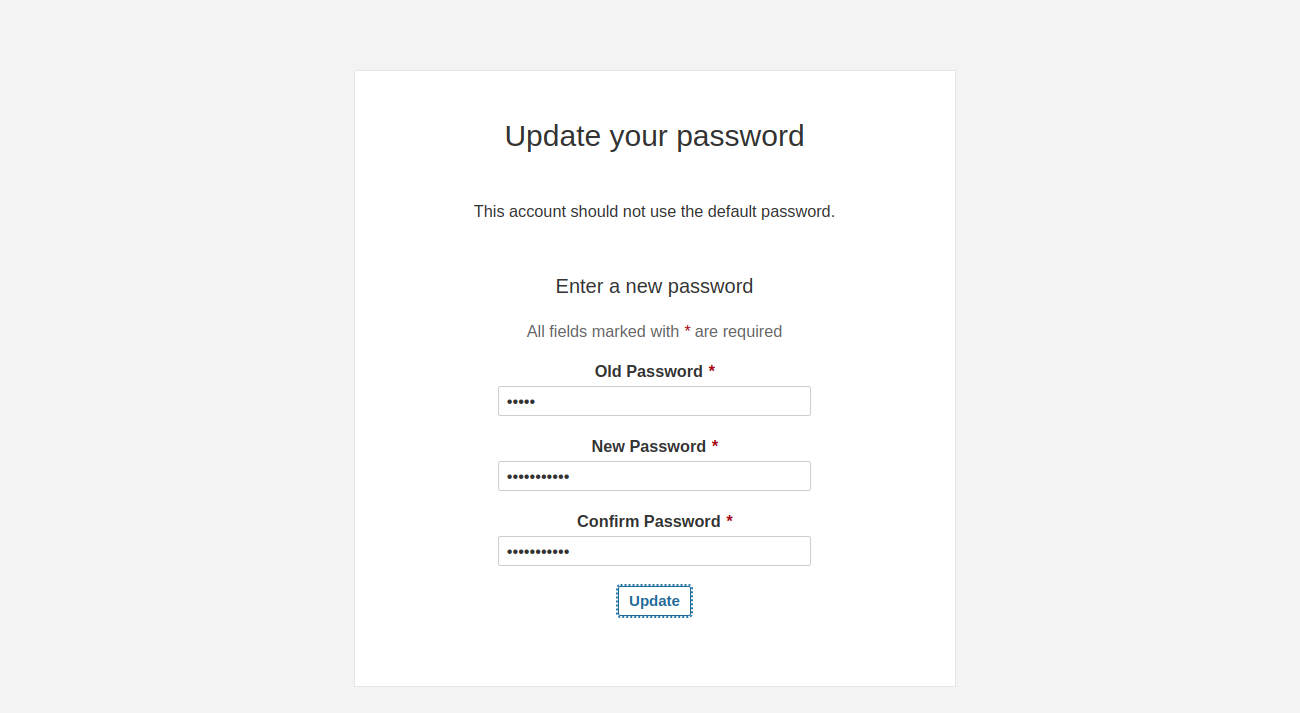
Provide the default username and password as admin/admin then click on the Log in button. You should see the password change screen.
Set your new admin password then click on the Update button. You should see the SonarQube dashboard on the following screen.
Conclusion
In this guide, we explained how to install the SonarQube tool on Fedora. You can now add your project from Git or another repository and start analyzing your code via a web-based interface. Try to install SonarQube on VPS hosting from Atlantic.Net!