Table of Contents
- Launching SFTP
- Changing Directories
- Displaying Remote Directories
- Quitting SFTP
- Downloading Files
- Displaying The Help Text
- Changing Local Directory
- Displaying Local Directory Listing
- Making A Local Directory
- Viewing Local Directory Listing
- Making Remote Directories
- Uploading Files
- Viewing Remote Working Directory
- Renaming Remote File
- Removing Remote Files
- Removing Remote Directory
- Escaping To The Local Shell
- What next?
Verified and Tested 08/31/15
Introduction
In this How-to, we will be going over the SFTP commands to make our lives easier and to work more effective in our shell sessions. SFTP is an acronym for “Secure File Transfer Protocol” and it is a secure way for file management over a network using SSH. Essentially it is FTP using SSH.
Prerequisites
– You need two Linux servers that configured with static IP addresses. One server to run the SFTP commands and one server to connect via SFTP.
Launching SFTP
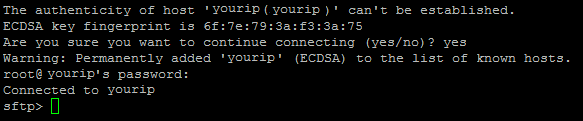
For this tutorial, we will be connecting via SFTP from one Linux Server to another. To launch SFTP, you will need two pieces of information. One is the remote username and the remote IP address or hostname of the server. Once you type the following command with that information, you will be prompted for the password. Then you will be logged in.
sftp remoteuser@remotehostorip
Changing Directories
Once you’re in, you can to run all the commands that you normally run. In this case, you can change from one directory to the other in your remote SFTP session with the following CD command:
cd
Displaying Remote Directories
You can view the directory listings for your remote SFTP session with any one of the following commands:
dir ls
Quitting SFTP
Once you are done with your remote SFTP session, you could close it with any of the following three commands:
exit quit bye
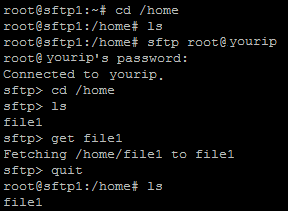
Downloading Files
You can download files from your remote session with the get command followed by the file that you wish to download. Do this with the following command and replacing the bracket and yourfile with the file of your choice.
get [yourfile]
Also, you could download it with a new name with the following command.(note: this will download to your local home directory)
get [yourfile] [newname]
Displaying The Help Text
If you don’t remember one of the SFTP commands, you can just type one of the following two commands to display them.
help ?
The output will be similar to the box below.
Available commands:
bye Quit sftp
cd path Change remote directory to 'path'
chgrp grp path Change group of file 'path' to 'grp'
chmod mode path Change permissions of file 'path' to 'mode'
chown own path Change owner of file 'path' to 'own'
df [-hi] [path] Display statistics for current directory or
filesystem containing 'path'
exit Quit sftp
get [-Ppr] remote [local] Download file
reget remote [local] Resume download file
help Display this help text
lcd path Change local directory to 'path'
lls [ls-options [path]] Display local directory listing
lmkdir path Create local directory
ln [-s] oldpath newpath Link remote file (-s for symlink)
lpwd Print local working directory
ls [-1afhlnrSt] [path] Display remote directory listing
lumask umask Set local umask to 'umask'
mkdir path Create remote directory
progress Toggle display of progress meter
put [-Ppr] local [remote] Upload file
pwd Display remote working directory
quit Quit sftp
rename oldpath newpath Rename remote file
rm path Delete remote file
rmdir path Remove remote directory
symlink oldpath newpath Symlink remote file
version Show SFTP version
!command Execute 'command' in local shell
! Escape to local shell
? Synonym for help
Changing Local Directory
You could also change your local systems directory from your remote session with the following command:
lcd
Displaying Local Directory Listing
To view any file that is located inside your local systems directory, run the following command:
lls
Making A Local Directory
To make a new directory in from your SFTP session to your local directory, type the following command replacing the bracket and newlocaldirectory.
lmkdir [newlocaldirectory]
Viewing Local Directory Listing
To see the local directory, not the remote directory that you are currently on, type the following command:
lpwd
Making Remote Directories
You can also make directories in your current remote SFTP session directory with the with the following command replacing the bracket and newremotedirectory.
mkdir [newremotedirectory]
Uploading Files
To upload files from your local system to your remote system, you could accomplish this with the put command followed by your local path and your remote path.
put [localfile] [remotefile]

Viewing Remote Working Directory
To view the current directory of your remote SFTP session, you can accomplish this with the following command:
pwd
Renaming Remote File
If you want to rename a file within your remote SFTP session, run the following command replacing the fileA(current name) and fileAnewname(new file name).
rename [fileA] [filenewname]
Removing Remote Files
To remove any files from your remote SFTP session, run the following rm command followed by the file you want to remove (in this example, fileA will be removed).
rm [fileA]
Removing Remote Directory
To remove any directory from your remote SFTP session, run the following rmdir command followed by the directory you want to (in this example, directoryA will be removed).
rmdir [directory]
Escaping To The Local Shell
If you would like to escape from your remote SFTP session and go to your local shell terminal, simply type the ! command to accomplish this.
!
What next?
Congratulations! This completes this tutorial on SFTP Commands. I hope that you found this information useful just like it was to me. Thank you for following along and feel free to check back with us for further updates,or to learn more about our VPS hosting solutions.