nload is a command-line tool used for monitoring network traffic and bandwidth usage in real-time. It will display the incoming and outgoing traffic using two graphs. This console-based application also displays info like the total amount of transferred data and min/max network.
In this post, we will show you how to install and use nload to monitor network bandwidth usage in real-time.
Step 1 – Install Nload
By default, nload is not installed on Linux operating system.
For Debian or Ubuntu operating system, install nload using the following command:
apt-get install nload -y
For CentOS or RHEL operating system, install nload using the following command:
yum install epel-release -y yum install nload -y
Step 2 – Use Nload to Monitor Network Usage
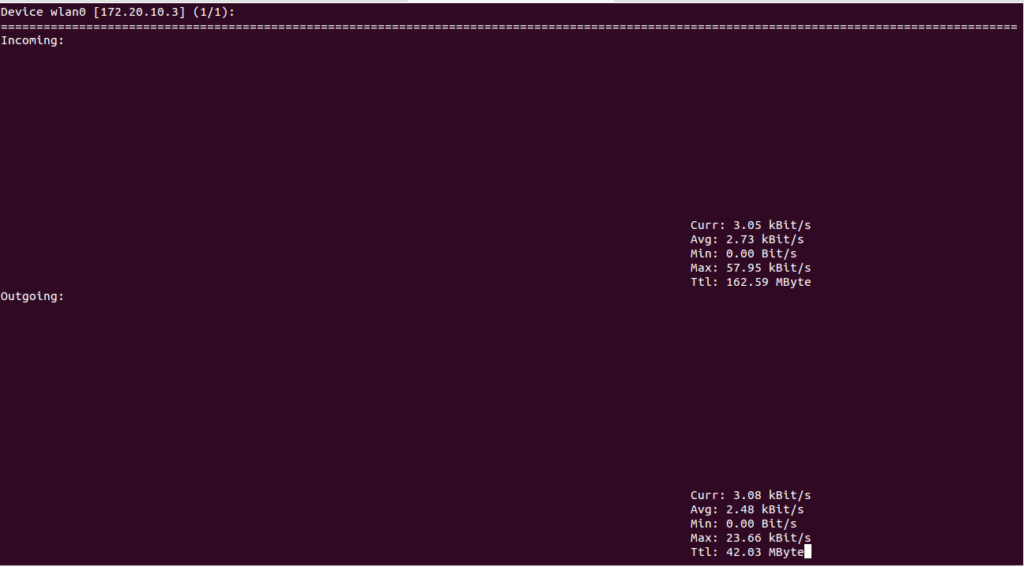
You can run the nload command by specifying a network interface. Otherwise, it will auto-detect the network interface and start monitoring.
nload wlan0
You should see the bandwidth usage on the wlan0 network interface on the following screen:
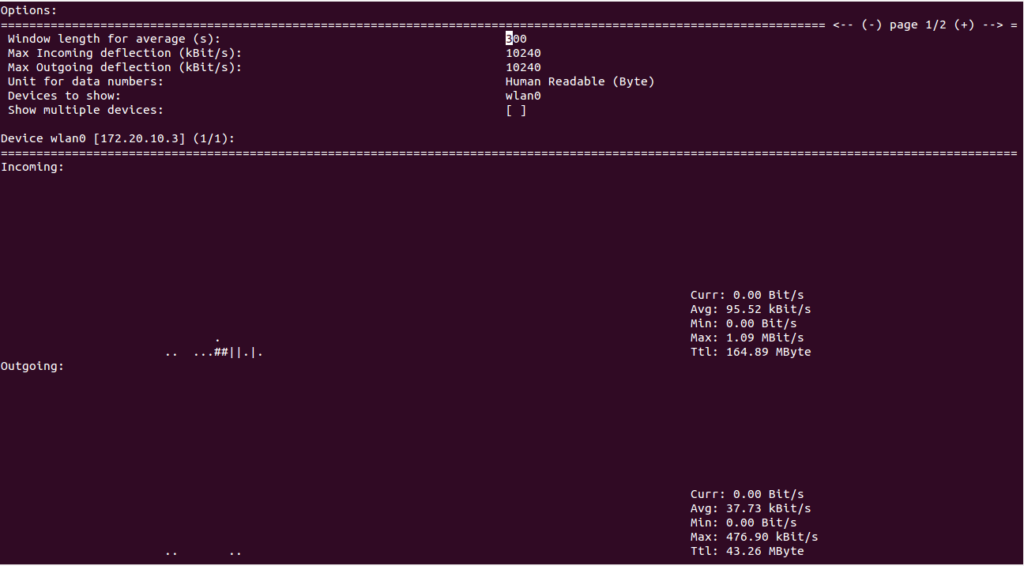
Press F2 to display the options windows:
Press F5 to save the current settings to the user’s configuration file.
Press F6 to reload settings from the user’s configuration file.
Press CTRL + C to close the nload window.
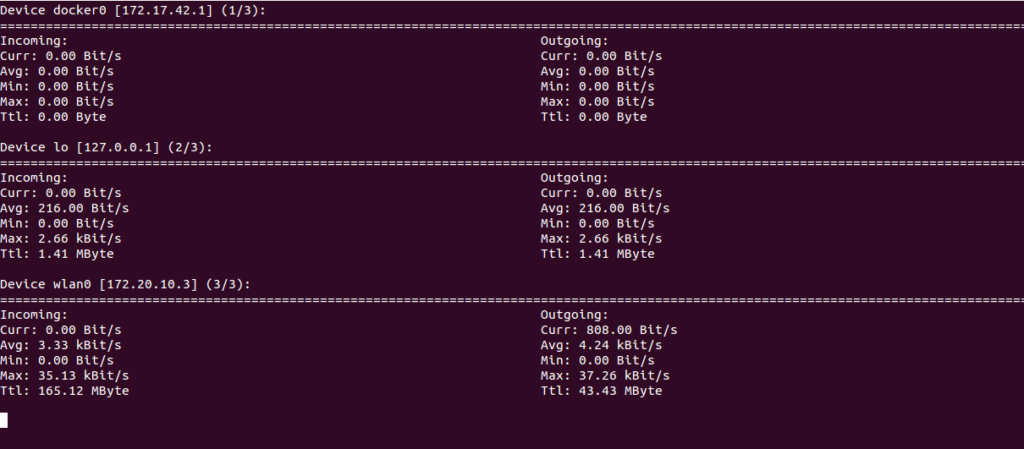
You can use the -m flag with nload command to display network usage of all network interfaces.
nload -m
You can use the -t flag to sets the refresh interval of the display in milliseconds.
nload -t 700 -m
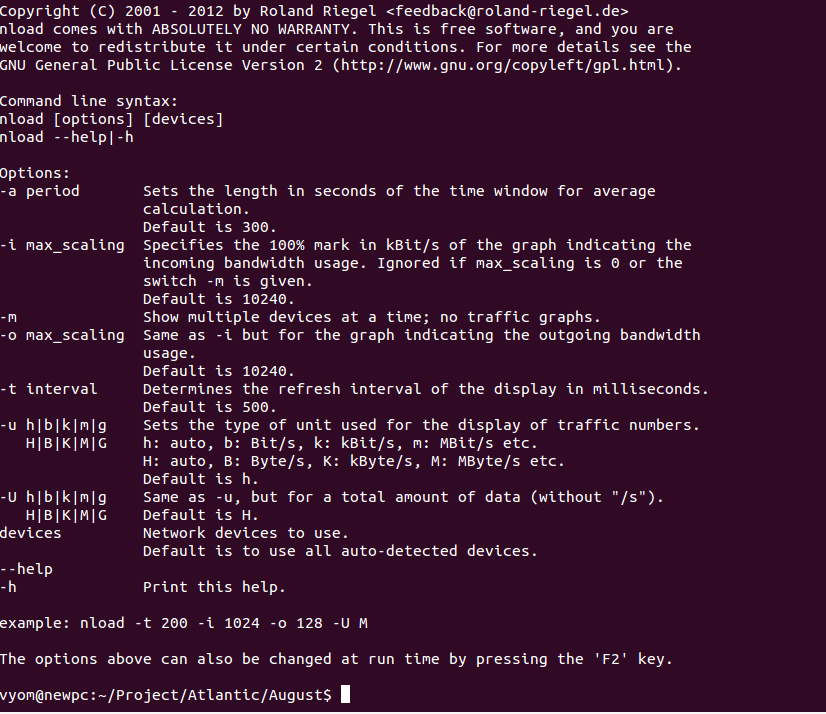
To display all options available with nload, run:
nload --help
You should see the Nload help page on the following screen:
Conclusion
In the above guide, you learned how to use the nload tool to monitor network usage in Linux. This tool will help you to monitor the network traffic and bandwidth usage in Linux. Get started today on your VPS hosting account from Altantic.Net.