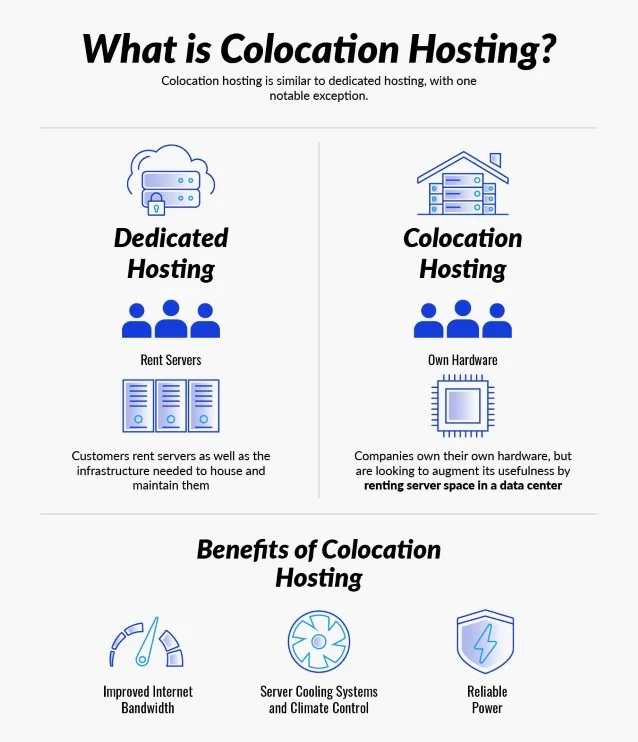
What is Colocation Hosting?
Colocation hosting is similar to dedicated hosting, with one notable exception.
In dedicated hosting, customers rent servers as well as the infrastructure needed to
house and
maintain them. In colocation hosting, companies own their own hardware, but are looking
to
augment its usefulness by renting server space in a data
center, which provides benefits like
improved Internet bandwidth, server cooling systems and climate control, and reliable
power.
Colocation hosting can be compared to owning a boat and renting a berth for it at the
closest
port of call. The boat remains in your possession and you can access it at any time, but
you’re
still enjoying the services of the port – including security for your vessel and the
ability to
use the facility’s equipment to maintain and get the most out of your boat.
This is part of an extensive series of guides about hybrid cloud.
How Colocation Hosting Works
In order to establish a colocation hosting arrangement, the customer must have their own physical server – one that they own. The customer isn’t renting a server from the hosting provider; rather, they are merely leasing space like they would at a rental storage company. The customer physically transports the server to the colocation hosting provider’s place of business, typically a data center. The customer only rents space within the data center or colocation site, but maintains ownership and control of all hardware and software settings for that server. By communicating with the colocation hosting provider’s team, the customer can quickly upgrade or downgrade features like bandwidth and rackspace to fit the business needs.
Colocation Hosting for Security
A top reason most companies employ colocation hosting is for the security it provides. While many former colocation users have made the move to cloud technology because of its ease of use, endless resources, and competitive pricing, there are some things cloud cannot do, according to Who’s Hosting This; primarily, it’s the level of control you have over your server compared to cloud.
Many industries, such as health care, have specific rules of compliance that must be met for legal purposes (like HIPAA and HITECH) when it comes to data and its privacy. Many industries’ rules state that data was be kept in a secure, on-site location, which colocation can provide because it is stored in the colocation provider’s secure data center. Your server is taken to the provider’s location and stored there securely while you pick and choose what services you wish to use, according to TechRadar.
Additional Benefits of Colocation Hosting
With colocation hosting, a small-to-midsized company can achieve a reasonable facsimile of enterprise-level hosting capabilities thanks to the shared hosting environment and on-site support. This can allow your company to play on a fairly even field when it comes to technology, even if it is a fraction of the size of the competition. Additional benefits include:
High bandwidth and low latency:Your server is plugged in to the colocation hosting provider’s network, giving it access to industrial-strength connection speeds. Additionally, you can contract with third-party providers like Spectrum or CenturyLink for even more connectivity options.
Unlimited power: No hosting situation is 100% free of risk, but you’re transferring the safety of your server from your office to a location built to prevent loss of electricity. A colocation hosting facility has access to steady power supplies, battery backups, and generators.
On-premises monitoring:Most data centers will employ security professionals or support technicians who monitor the premises 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, and 365 days a year for unauthorized visitors. They control who has access to the data center.
Advanced climate control systems: Maintaining the perfect temperature and humidity requirements for servers to operate at optimal efficiency can be a tricky balance to achieve. A colocation hosting facility will have tailored climate control systems that allow the data center managers to properly maintain ideal environmental conditions.
Live monitoring of equipment: In a typical office, your first indication that hardware is in need of maintenance, update, or replacement is when something fails, slowing or stopping your employees’ production. With colocation hosting, IT professionals are monitoring your equipment constantly to ensure it is performing optimally.
Better management:In your own brick-and-mortar location, your servers might be managed by a contract IT person, a part-time worker, or a full-time employee who wears several different hats.
Upgrading or downloading your server’s capabilities in this environment involves lots of moving parts. When using a colocation hosting provider, a simple email or phone call will perform the same work, without adding to your budget or reducing employee productivity.
Negatives of Colocation Hosting
Several of the positives of colocation hosting rest in the same space as one of the negatives: If you want to replace your server or make changes to it personally, it requires driving to the colocation facility and having the staff remove it for you. Even done quickly, this is a process that effectively takes your business offline for at least a few minutes. Additionally, many colocation providers have locked in prices on the cost of electricity and bandwidth that you pay for several months of uninterrupted service. Should you choose this course and then prices for either service fall, you’ll be stuck paying the locked-in price.
See Additional Guides on Key Hybrid Cloud Topics
Together with our content partners, we have authored in-depth guides on several other topics that can also be useful as you explore the world of hybrid cloud.Cloud Migration
Authored by Faddom- [Guide] Data Center Migration: Complete Guide 2025
- [Guide] Cloud Migration to AWS: 3 Phases, 7 Rs and 5 Free Tools to Get You Started
- [Blog] How Secure is the Cloud?
- [Product] Faddom | Instant Application Dependency Mapping Tool
Nutanix
Authored by Faddom- [Guide] Nutanix: History, Products, and Top 5 Alternatives -
- [Guide] Nutanix vs. VMware: 5 Key Differences and How to Choose
- [Product] Faddom | Instant Application Dependency Mapping Tool
